Category: Cardiology
Keywords: athlete, ventricular hypertrophy (PubMed Search)
Posted: 4/8/2012 by Amal Mattu, MD
Click here to contact Amal Mattu, MD
(Pearl provided by Dr. Semhar Tewelde)
Physiological LV hypertrophy in trained athletes is defined by an isolated increase in QRS amplitude, normal axis, normal atrial and ventricular activations patterns, and normal ST-segment T-wave replorization; athletes of African/Caribbean descent have prominent cardiovascular remodeling leading to pronounced voltage criteria for LV hypertrophy and BER
Despite the presence of voltage criteria for LVH, pure QRS voltage criteria for LVH in an asymptomatic athlete without family hx of cardiovascular diseases or SCD, and lack of non-voltage ECG criteria does not warrant systematic evaluation with echocardiography.
In other words, young patients, especially men, especially those of African/Caribbean descent, will be expected to have large voltage QRS complexes and sometimes abnormal repolarization, and this is not necessarily a pathologic finding.
Corrado D, Pelliccia A, Heidbuchel H, et al. Recommendations for interpretation of 12-lead electrocardiogram in the athlete. European heart journal. Jan 2010; 31(2):243-259
Category: Orthopedics
Keywords: stress fracture, shin splints (PubMed Search)
Posted: 4/7/2012 by Brian Corwell, MD
(Updated: 2/7/2026)
Click here to contact Brian Corwell, MD
Exertional leg pain in the athlete carries a wide range of possible etiologies. In a recent review article, etiologies included, stress fracture (25%), exertional compartment syndrome (33%), medial tibial stress syndrome (13%), nerve entrapment (10%), and popliteal artery entrapment syndrome.
Medial Tibial Stress Syndrome (MTSS) is also known as shin splints. It is a repetitive-stress overuse injury.
Risk factors include: hyperpronation, higher BMI, increased hip internal rotation, and hyperplantar flexion.
While MTSS may be on a stress reaction spectrum that includes fracture, the causes are likely to also include tendinopathy and muscle dysfunction (tibialis anterior, posterior and soleus).
Radiographs will be normal with this condition. MRI and bone scan may show signal abnormality along the posterior medial tibial surface.
Treatment: In most cases participation in sports may continue. Also consider, rest/activity modification, ice, NSAIDs, physical therapy for calf stretching and strengthening, and rigid orthotics (to correct foot hyperpronation). Semi rigid and neoprene orthotics may be considered for prevention in those with a prior history.
Category: Pharmacology & Therapeutics
Keywords: vancomycin, c. diff, clostridium difficile, fidaxomicin (PubMed Search)
Posted: 4/4/2012 by Bryan Hayes, PharmD
(Updated: 4/7/2012)
Click here to contact Bryan Hayes, PharmD
In a recent multicenter, double-blind, randomized, non-inferiority trial, vancomycin was compared to fidaxomixin for Clostridium difficile infection.
Location: 45 sites in Europe and 41 sites in the USA and Canada
Patients: Age 16 years or older with acute toxin-positive C difficile infection.
Treatment: Oral fidaxomicin (200 mg every 12 h) or oral vancomycin (125 mg every 6 h) for 10 days.
Endpoint: Clinical cure, defined as resolution of diarrhea and no further need for treatment.
Results: 198 (91.7%) of 216 patients in the per-protocol population given fidaxomicin achieved clinical cure, compared with 213 (90.6%) of 235 given vancomycin (one-sided 97·5% CI -4·3%). Occurrence of treatment-emergent adverse events did not differ between groups.
Author conclusions: Fidaxomicin could be an alternative treatment for infection with C difficile, with similar efficacy and safety to vancomycin.
Funding: Optimer Pharmaceuticals.
Cornely OA, Crook DW, Esposito R, et al. Fidaxomicin versus vancomycin for infection with Clostridium difficile in Europe, Canada, and the USA: a double-blind, non-inferiority, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Infect Dis 2012 Apr;12(4):281-9.
Follow me on Twitter (@pharmacytoxguy)
Category: Pediatrics
Keywords: electrical injury, EKG (PubMed Search)
Posted: 4/6/2012 by Mimi Lu, MD
Click here to contact Mimi Lu, MD
It is likely that during ones career in Emergency Medicine, one will be faced with how to work up a child presenting to the ER following exposure to common house electrical current. The older recommendations were such that all children exposed, received a screening EKG and were admitted to telemetry for monitoring. However, a relatively recent article in the Annals of Emergency Medicine suggests otherwise.
In fact, after reviewing several studies the authors conclude that, although there is not enough literature to support evidence based practice “guidelines”, there appears to enough evidence to support that practice of “safely discharging these children without an initial EKG evaluation or inpatient cardiac monitoring after a common household current exposure.” This includes both 120V and 220 V exposures.
Clearly, some patients may require work up and/or admission based on other injuries or clinical presentation.
References:
Chen E H, Sareen A, Do Children Require ECG Evaluation and Inpatient Telemetry After Household Electrical Exposures? Ann Emerg Med. 2007;49:64-67.
Category: Toxicology
Keywords: protamine, enoxaparin, Xa (PubMed Search)
Posted: 4/5/2012 by Ellen Lemkin, MD, PharmD
Click here to contact Ellen Lemkin, MD, PharmD
Protamine for enoxaparin overdose
Category: Critical Care
Posted: 4/3/2012 by Mike Winters, MBA, MD
Click here to contact Mike Winters, MBA, MD
Transferring Multidrug-Resistant Organisms
Morgan DJ, et al. Transfer of multidrug-resistant bacteria to healthcare workers' gloves and gowns after patient contact increases with environmental contamination. Crit Care Med 2012; 40:1045-1051.
Category: Cardiology
Keywords: athlete, electrocardiogram, electrocardiography (PubMed Search)
Posted: 4/1/2012 by Amal Mattu, MD
(Updated: 2/7/2026)
Click here to contact Amal Mattu, MD
Pearl provided by Dr. Semhar Tewelde
The Athlete's Heart and ECG Abnormalities
Up to 80% of athletes have common training related ECG changes/abnormalities including: sinus bradycardia, asymptomatic sinus pause, sinus arrhythmia, first degree AV block, incomplete right bundle branch block, benign early repolarization (BER), and isolated QRS voltage criteria for left ventricular (LV) hypertrophy.
Approximately 5% athletes exhibit uncommon training unrelated ECG changes/abnormalities including: T-wave inversions, ST-depression, pathological Q-waves, left axis deviation/left anterior fasicular block, right axis deviation/left posterior fasicular block, right ventricular hypertrophy, complete left or right bundle branch block, long or short QT interval, ventricular pre-excitation/WPW, Brugada pattern, and arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia (ARVD).
Corrado D, Pelliccia A, Heidbuchel H, et al. Recommendations for interpretation of 12-lead electrocardiogram in the athlete. European heart journal. Jan 2010; 31(2):243-259
Category: Pediatrics
Posted: 3/31/2012 by Rose Chasm, MD
(Updated: 2/7/2026)
Click here to contact Rose Chasm, MD
2012 Pediatrics Review and Education Program
Category: Toxicology
Keywords: epinephrine, carbon monoxide, smoke inhalation (PubMed Search)
Posted: 3/29/2012 by Fermin Barrueto
(Updated: 2/7/2026)
Click here to contact Fermin Barrueto
Animal studies can pave the way for new clinical treatment modalities. In the setting of lung injury due to smoke inhalation, one of the problems (if you can get the ET tube in) are the elevated ventilatory pressures due to the massive edema. In this sheep model of smoke inhalation, nebulized epinephrine improved ventilatory pressures, PaO2/FiO2 ratio and pulmonary shunting.
We may have these sheep to thank for this new treatment.
Lange M, Hamahata A, Traber DL, Cox RA, Kulp GA, Nakano Y, Traber LD, Herndon DN, Enkhbaatar P.
Crit Care Med. 2011 Apr;39(4):718-24.
Category: Critical Care
Keywords: apnea time, rapid sequence intubation, atelectasis, crticial care, intubation, hypoexemia, obesity (PubMed Search)
Posted: 3/26/2012 by Haney Mallemat, MD
(Updated: 3/27/2012)
Click here to contact Haney Mallemat, MD
The supine position during rapid sequence intubation may result in posterior lung atelectasis thereby reducing lung volumes, oxygenation reserve, and ultimately apnea time.
Several studies have shown that elevating the head of the bed by at least 20 degrees or placing a patient in reverse Trendelenberg position (for patients with contra-indications to elevating the head of the bed) during RSI may significantly increase apnea time.
Elevating the head of the bed may be especially helpful for patients with BMIs >35
Weingart, S and Levitan, R. Preoxygenation and prevention of desaturation during emergency airway management. Ann Emerg Med. 2012 Mar; 59(3):165-175.e1; here's the article for FREE: http://www.annemergmed.com/article/S0196-0644(11)01667-2/fulltext
Follow me on Twitter (@criticalcarenow) or Google+ (+haney mallemat)
Category: Visual Diagnosis
Posted: 3/25/2012 by Haney Mallemat, MD
(Updated: 3/26/2012)
Click here to contact Haney Mallemat, MD
26 year old male with pain when he extends his 4th finger as well as swelling of that digit. Diagnosis?
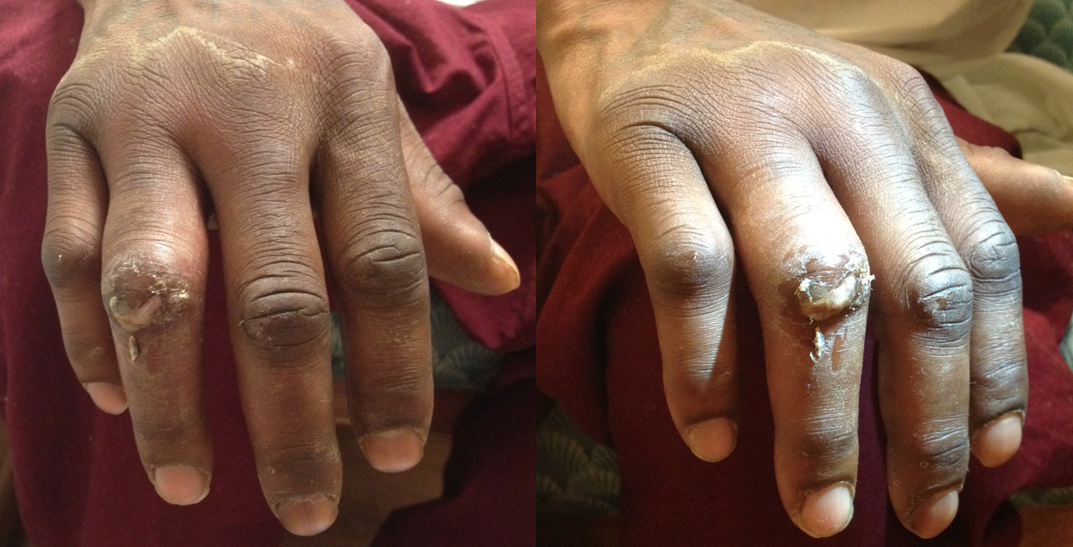
Answer: Infectious Flexor Tenosynovitis
Infectious Flexor Tenosynovitis
- Closed space infection of the flexor tendon sheath; an orthopedic emergency
- Typically an infection with skin flora secondary to penetrating trauma
- Diagnosed by Kanavel's Signs:
- Finger held in slight flexion
- Fusiform swelling
- Pain on passive extension
- Pain while palpating the tendon sheath
- If early and not severe a course of IV antibiotics (covering skin flora) may be tried, however, surgical intervention is often necessary; early consultation with a hand surgeon is highly recommended
Follow me on Twitter (@criticalcarenow) or Google+ (+haney mallemat)
Category: Cardiology
Keywords: hypothermia, cardiogenic shock (PubMed Search)
Posted: 3/25/2012 by Amal Mattu, MD
(Updated: 2/7/2026)
Click here to contact Amal Mattu, MD
Cardiogenic shock pearls from Dr. Semhar Tewelde:
1. CS is most commonly secondary to a large MI where > 40% of the myocardium is involved; however mechanical, valvular, dysrhythmogenic, and infectious etiologies should also be considered: papillary or chordal dysfunction, free wall or septal defects disease, insuffiency of any valve, myopericarditis, endocarditis, Tako-tsubo, end stage cardiomyopathy, and tamponade.
2. Incidence of 5-10% STEMI and 2.5-5% NSTEMI
3. Mortality ~50%
4. Immediate coronary reperfusion is the best treatment (NNT 8). Medical therapy is a distant second choice in management, with reperfusion and pressors as needed. Early intra-aortic balloon pump use is key.
5. Recent case reports have shown imporved outcomes when induced hypothermia was used in patients refractory to traditional therapy with pressors/inotropes/IABP.
Category: Orthopedics
Keywords: cardiac arrest, exercise, marathon (PubMed Search)
Posted: 3/24/2012 by Brian Corwell, MD
(Updated: 2/7/2026)
Click here to contact Brian Corwell, MD
A recent study looked at the risk of sudden cardiac death during a marathon.
Many isolated reports of sudden death make headlines in the national news.
However, of nearly 11 million runners, only 59 went into cardiac arrest during a race. This equates to an incidence rate of 0.54 per 100,000 participants,
This rate appears to be on par with sudden death from other athletic endeavors such as triathlons and college athletics.
Median age was 42. Men affected more than women (men also more likely to die from the event).
71% of events were fatal.
Further, risk is greater for both cardiac arrest and sudden death for full marathons than half marathons.
Interestingly, older patients fared better (increased survival in those >40yo), thought to be due to an increased incidence of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy in younger aged runners.
Baggish et al., New England Journal of Medicine.
Category: Pediatrics
Keywords: orthopedics (PubMed Search)
Posted: 3/23/2012 by Mimi Lu, MD
Click here to contact Mimi Lu, MD
Patellar dislocations:
References:
1. http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/90068-overview
2. New England Musculoskeletal Institute. http://nemsi.uchc.edu/clinical_services/orthopaedic/knee/patellar_dislocation.html
Category: Critical Care
Posted: 3/20/2012 by Mike Winters, MBA, MD
(Updated: 2/7/2026)
Click here to contact Mike Winters, MBA, MD
High-Frequency Oscillatory Ventilation for ARDS?
Ip T, Mehta S. The role of high-frequency oscillatory ventilation in the treatment of acute respiratory failure in adults. Curr Opin Crit Care 2012; 18:70-9.
Category: Medical Education
Keywords: education, whiteboards (PubMed Search)
Posted: 3/12/2012 by Rob Rogers, MD
(Updated: 2/7/2026)
Click here to contact Rob Rogers, MD
Every heard of the Khan Academy website? If you have, you will instantly recogize what a powerful force this website has become in education. If you haven't, what are you waiting for? Head to http://www.khanacademy.org/ and check it out! This site gets millions of hit PER DAY.
The Khan Academy was developed by, guess who, a guy named Kahn, Salman Kahn. This website is amazing. My kids use it for some of their school work. Trust me, check it out. If you want to know just how good this guy is...check out the size of the check Bill Gates wrote him.
What does this have to do with medical education? The videos put together by Khan utilize a teaching modality called a "whiteboard." This type of teaching technology is changing they way educators deliver material. Programs like Doceri (www.doceri.com) utilize this concept. You can build presentations and teaching materials with audio included.
My pearl for you today is really more of an assignment...go to the two websites and check them out. First, visit the Khan Academy site and then the Doceri site. THIS kind of thing is the future of education...
Category: Cardiology
Keywords: coronary artery disease, young, acute coronary syndromes (PubMed Search)
Posted: 3/18/2012 by Amal Mattu, MD
(Updated: 2/7/2026)
Click here to contact Amal Mattu, MD
How likely is coronary artery disease to occur in young patients?
An autopsy series in US communities evaluated young patients (avg age 36 years old) who died of "non-natural" causes revealed coronary atherosclerosis in > 80% of the autopsy sample, with 8% having significant obstructive disease.
The bottom line is simple....be wary of discounting the risk of ACS purely based on a patient's age. The HPI is the most important factor in predicting ACS.
Nemetz PN, et al. Recent trends in the prevalance of coronary disease: a population-based autopsy study of nonnatural deaths. Arch Intern Med 2008;168:264-270.
Arbab-Zadeh A, et al. Acute coronary events. Circulation 2012;125:1147-1156.
Category: Pediatrics
Posted: 3/16/2012 by Mimi Lu, MD
Click here to contact Mimi Lu, MD
Rashes that include palms/ soles
- Hand-Foot-Mouth Disease
- Kawasaki
- Erythema multiforme/ Stevens Johnson's Syndrome/ Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis
- Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever
- Scabies
- Syphillis
Rashes that have +Nikolsky's sign
- Scalded Skin Syndrome
- TEN
- Pemphigus Vulgaris
Rashes that desquamate
- Scalded Skin Syndrome
- Toxic Shock Syndrome
- Scarlet Fever
- Kawasaki
- TEN
Category: Toxicology
Keywords: ticagrelor, brillinta, xarelto, pradaxa (PubMed Search)
Posted: 3/15/2012 by Fermin Barrueto
(Updated: 2/7/2026)
Click here to contact Fermin Barrueto
Coumadin Wannabe's - have indication non-valvular atrial fibrillation
1) Dabigatran (Pradaxa)
2) Rivaroxaban (Xarelto)
Clopidogrel Wannabe's - both are antiplatelets
1) Ticagrelor (Brilinta)
2) Prasugrel (Effient)
If you were looking for the first case reports of lethal hemorrhage due to pradaxa that could not be reversed - look no further. One patient fall from standing dies from ICH and another death in a spine trauma patient on pradaxa. I am waiting for the first epidural hematoma due to pradaxa, xarelto, etc in ED. Watch out! :
1: Garber ST, Sivakumar W, Schmidt RH. Neurosurgical complications of direct thrombin inhibitors-catastrophic hemorrhage after mild traumatic brain injury in a patient receiving dabigatran. J Neurosurg. 2012 Mar 6. 2: Truumees E, Gaudu T, Dieterichs C, Geck M, Stokes J. Epidural Hematoma & Intra-operative Hemorrhage in a Spine Trauma Patient on Pradaxa® [Dabigatran]. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2012 Feb 16.
Category: Critical Care
Posted: 3/13/2012 by Haney Mallemat, MD
(Updated: 3/14/2012)
Click here to contact Haney Mallemat, MD
Pre-oxygenation prior to rapid sequence intubation (RSI) is performed to prevent hypoxemia during endotracheal intubation.
An appropriate period of pre-oxygenation will potentially increase the amount of apnea time during intubation, however patients with certain critical illnesses (e.g., severe pneumonia) may desaturate faster than expected.
Apnea time can be increased by maintaining high-flow oxygen by nasal cannula (e.g., 15L), during application of the bag-valve mask and during the time of attempted endotracheal tube placement; this concept is known as apneic oxygenation.
Apneic oxygenation is based on the principle that when patients are apneic, alveoli absorb oxygen into the blood stream at a rate of approximately 250 mL/minute, creating a diffusion gradient from the pharynx (containing a high-density of oxygen from the nasal cannula) to a lower concentration of oxygen in the alveoli.
Although a patient’s oxygenation can be maintained longer using apneic oxygenation, its application does not remove the continuous buildup of CO2 in the alveoli during apena. Therefore, respiratory acidosis can result after a prolonged period of apneic oxygenation.
The complete article describing the physiology and practical applications can be found here....it's free! http://www.annemergmed.com/article/S0196-0644(11)01667-2/fulltext
Weingart, S and Levitan, R. Preoxygenation and prevention of desaturation during emergency airway management. Ann Emerg Med. 2012 Mar; 59(3):165-175.e1
Follow me on Twitter (@criticalcarenow) or Google+ (+haney mallemat)
