Category: Critical Care
Keywords: Acute pulmonary edema, Bolus nitrates (PubMed Search)
Posted: 12/27/2016 by Rory Spiegel, MD
(Updated: 2/8/2026)
Click here to contact Rory Spiegel, MD
It is well known that the early aggressive utilization of IV nitrates and non-invasive positive pressure ventilation (NIV) in patients presenting with acute pulmonary edema will decrease the number of patients requiring endotracheal intubation and mechanical ventilation.
Often our tepid dosing of nitroglycerine is to blame for treatment failure. Multiple studies have demonstrated the advantages of bolus dose nitroglycerine in the early management of patients with acute pulmonary edema. In these cohorts, patients bolused with impressively high doses of IV nitrates every 5 minutes, are intuabted less frequently than patients who received a standard infusion (1,2). No concerning drops in blood pressure in the patients who received bolus doses of nitrates were observed. Using the standard 200 micrograms/ml nitroglycerine concentration, blood pressure can be rapidly titrated to effect.
1. Cotter G, Metzkor E, Kaluski E, et al. Randomised trial of high-dose isosorbide dinitrate plus low-dose furosemide versus high-dose furosemide plus low-dose isosorbide dinitrate in severe pulmonary oedema. Lancet. 1998;351(9100):389-93.
2. Levy P, Compton S, Welch R, et al. Treatment of severe decompensated heart failure with high-dose intravenous nitroglycerin: a feasibility and outcome analysis. Ann Emerg Med. 2007;50(2):144-52
Category: Visual Diagnosis
Posted: 12/27/2016 by Tu Carol Nguyen, DO
Click here to contact Tu Carol Nguyen, DO
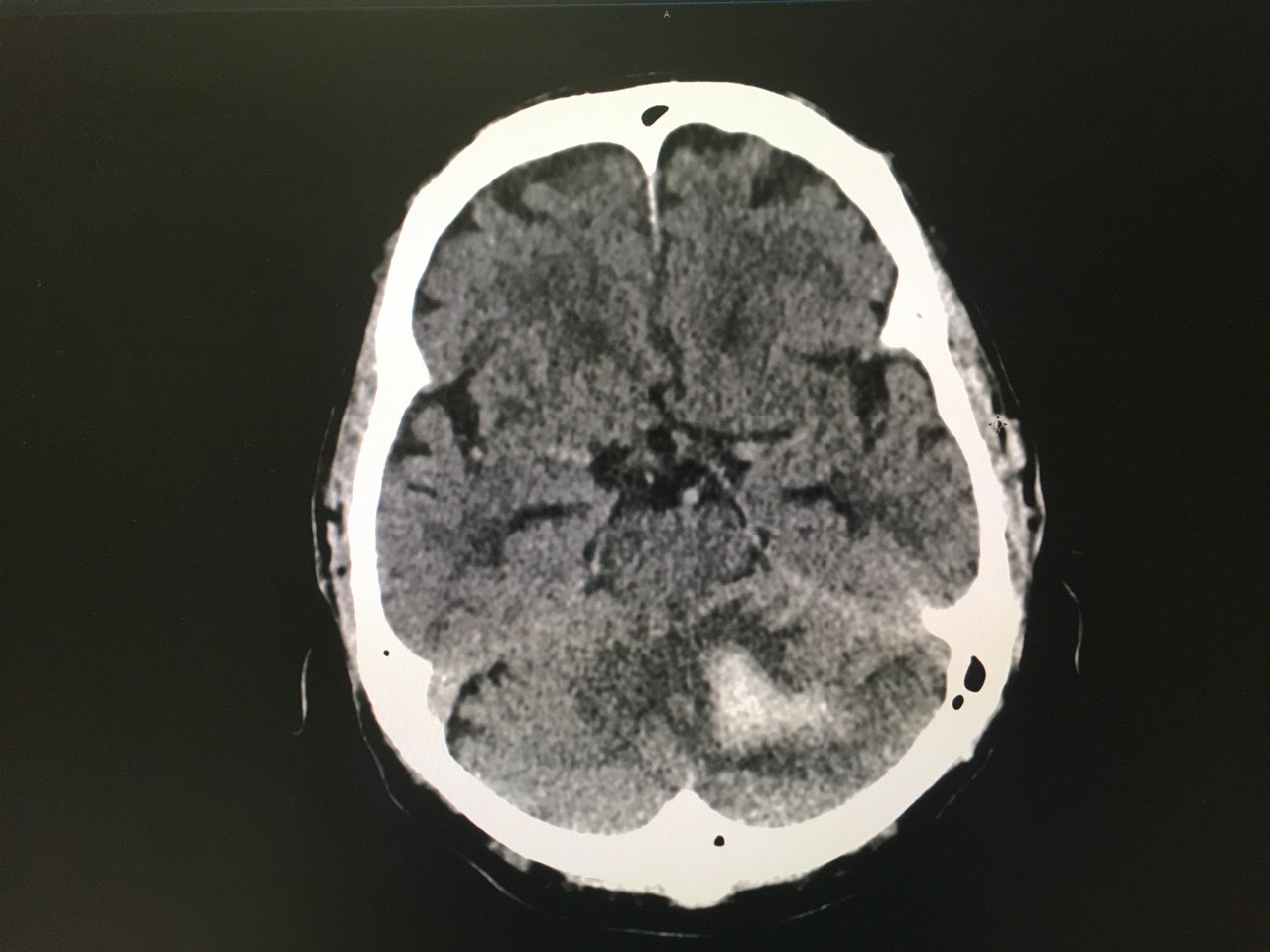
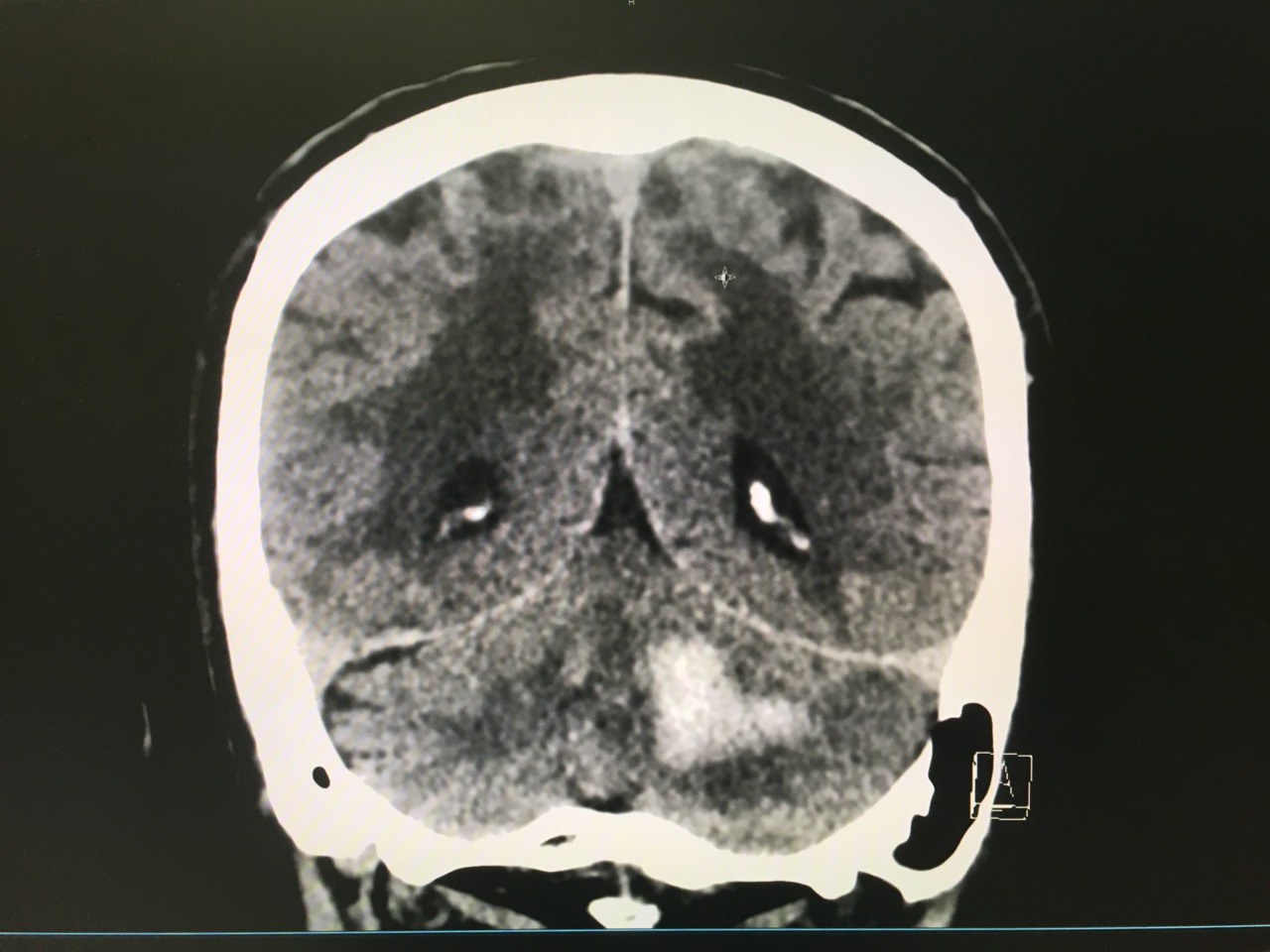
Answer: Large left cerebellar intraparenchymal hemorrhage with surrounding vasogenic edema with mild infratentorial midline shift of ~4mm
Take Home Points:
Hemphill JC, Greenberg SM, Anderson CS, et al. Guidelines for the Management of Spontaneous Intracerebral Hemorrhage: A Guideline for Healthcare Professionals From the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2015;46(7):2032-60.
Category: Orthopedics
Keywords: Concussions, musculoskeletal injury (PubMed Search)
Posted: 12/24/2016 by Brian Corwell, MD
Click here to contact Brian Corwell, MD
Significant associations were found between concussion and
Lateral ankle sprain (P = 0.012)
Knee injury (P = 0.002)
Lower extremity muscle injury (P = 0.031)
Keep in mind that 50 – 80% of concussions may go undiagnosed or unreported.
A discussion about risks of early return after concussion should include mention of risks beyond repeat head injury/2nd impact syndrome
Study limits: Retrospective design limits ability to establish causation/reporting bias
Gilbert, Burdette, et al., 2016 Association between concussion and lower extremity injuries in collegiate athletes. Sports Health 8 (6), 561-567.
Category: International EM
Keywords: Vitamin B12, pernicious anemia (PubMed Search)
Posted: 12/21/2016 by Jon Mark Hirshon, MPH, MD, PhD
Click here to contact Jon Mark Hirshon, MPH, MD, PhD
Vitamin B12 deficiency, including pernicious anemia, is typically seen in malnourished individuals. Globally, it is widespread in those who live in poverty.
In the U.S., we often consider it in individuals who are chronic alcoholics. However, it can be seen in others, including:
Category: Critical Care
Keywords: Intracranial hemorrhage, ICH, PCC, FFP, vitamin K antagonist, VKA, coumadin, warfarin (PubMed Search)
Posted: 12/20/2016 by Daniel Haase, MD
(Updated: 2/18/2017)
Click here to contact Daniel Haase, MD
The Neurocritical Care Society and Society of Critical Care Medicine just came out with new Guidelines for Reversal of Antithrombotics in Intracranial Hemorrhage (ICH) [1]
--PCC is now recommended over FFP in reversal of vitamin K antagonists (VKA) with elevated INR. Either should be co-administered with 10mg IV vitamin K. (Strong recommendation, moderate quality evidence)
TAKE AWAY: PCC should be probably be given over FFP in VKA-ICH when available
--Seems to be primarily based on a recent Lancet trial, which was stopped early due to safety concerns [2], but demonstrated more rapid reversal of INR and less hematoma expansion.
--In that study, all hematoma expansion related deaths occurred in the FFP group.
--Study was not designed to look at 90 day outcome, but trended towards improved survival.
1. Guideline for Reversal of Antithrombotics in Intracranial Hemorrhage: Executive Summary. A Statement for Healthcare Professionals From the Neurocritical Care Society and the Society of Critical Care Medicine. Frontera JA, Lewin JJ 3rd, et al. Crit Care Med. 2016 Dec;44(12):2251-2257.
2. Fresh frozen plasma versus prothrombin complex concentrate in patients with intracranial haemorrhage related to vitamin K antagonists (INCH): a randomised trial. Steiner T, Poli S, et al. Lancet Neurol. 2016 May;15(6):566-73.
Category: Infectious Disease
Keywords: cellulitis (PubMed Search)
Posted: 12/15/2016 by Michael Bond, MD
(Updated: 12/17/2016)
Click here to contact Michael Bond, MD
Take home points:
Category: Pediatrics
Keywords: fever, diarrhea, urinary tract infection (PubMed Search)
Posted: 12/16/2016 by Jenny Guyther, MD
(Updated: 2/8/2026)
Click here to contact Jenny Guyther, MD
After 4 months old, the answer MAY be no.
80 children between 4 months and 6 years of age with fever > 101 degress F and watery stools (> 3 episodes) were evaluated for hydration status using urine samples. The urine was collected either by catheterization or clean catch, depending on age. All urine cultures were negative.
Nibhanipudi KV. A Study to determine the Incidence of Urinary Tract Infections in Infants and Children Ages 4 months to 6 Years with Febrile Diarrhea. Glob Pediatr Health. 2016. Published online Sept 12, 2016.
Category: Toxicology
Keywords: Acetaminophen, Liver Failure (PubMed Search)
Posted: 12/16/2016 by Kathy Prybys, MD
Click here to contact Kathy Prybys, MD
Acetaminophen is one of the most common pharmaceutical ingestions in overdose and a leading cause of acute of liver failure in the U.S. Early recognition and treatment is critical for prevention of morbidity.
Category: Neurology
Keywords: pharmacist, thrombolysis, door-to-needle time, acute ischemic stroke (PubMed Search)
Posted: 12/14/2016 by WanTsu Wendy Chang, MD
Click here to contact WanTsu Wendy Chang, MD
Impact of an ED pharmacist on time to thrombolysis in acute ischemic stroke
Montgomery K, Hall AB, Keriazes G. Impact of an emergency medicine pharmacist on time to thrombolysis in acute ischemic stroke. Am J Emerg Med 2016;34:1997-9.
Follow me on Twitter @EM_NCC
Category: Critical Care
Posted: 12/13/2016 by Mike Winters, MBA, MD
Click here to contact Mike Winters, MBA, MD
Mechanical Ventilation in the Obese Patient
Goyal M, et al. Body mass index is associated with inappropriate tidal volumes in adults intubated in the ED. Am J Emerg Med 2016; 34:1682-3.
Category: Visual Diagnosis
Posted: 12/12/2016 by Hussain Alhashem, MBBS
Click here to contact Hussain Alhashem, MBBS
30 Year-old female presents to the ED for a rash. The rash started suddenly, mainly in her extremities and it is painful. The patient denied having fever or chills. Her past medical history is unremarkable. She admits to using cocaine frequently. The rash is shown in the picture.
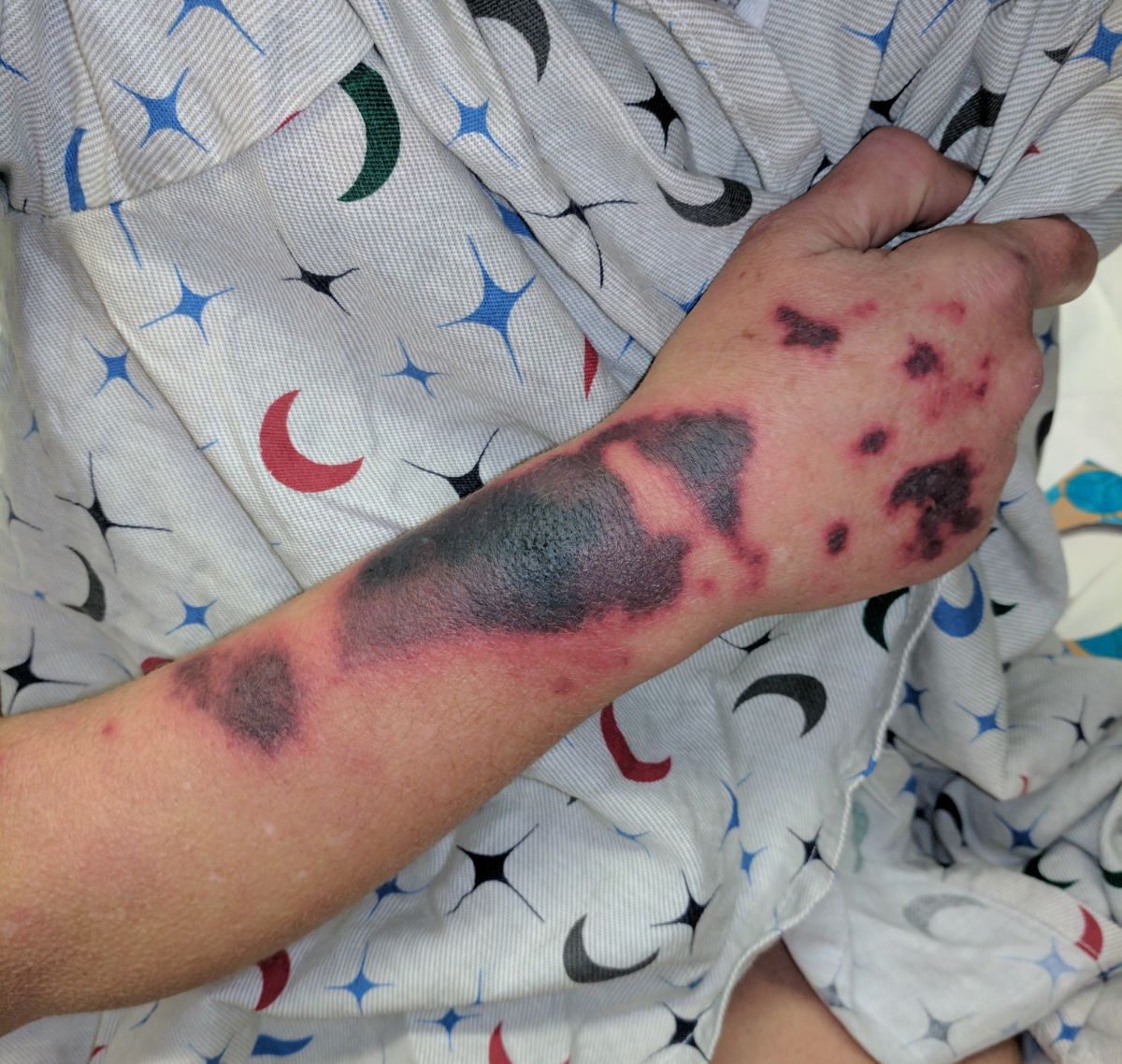
Levamisole-Induced Vasculitis
- Levamisole is an antihelmintic drug that was banned by the US Food and Drug Administration in 2000 because of its adverse effects.
- It is added to cocaine to increase its weight and potentiate its effect.
- Patients usually present with painful purpuric rash without central necrosis.
- Laboratory values might include agranulocytosis and elevated ESR.
- Treatment is by cessation of cocaine use.
- Because Levamisole is strongly associated with agranulocytosis, corticosteroids should be avoided to prevent immunosuppression.
Roberts, Jordan A., and Patricia Chévez-Barrios. "Levamisole-induced vasculitis: a characteristic cutaneous vasculitis associated with levamisole-adulterated cocaine." Archives of pathology & laboratory medicine 139.8 (2015): 1058-1061.
Category: Toxicology
Keywords: acetaminophen overdose, APAP levels (PubMed Search)
Posted: 12/8/2016 by Hong Kim, MD
(Updated: 12/9/2016)
Click here to contact Hong Kim, MD
Recent study evaluated whether an acetaminophen (APAP) level obtained less than 4-hour post acute ingestion can predict which patient would not require n-acetylcysteine (NAC). APAP cutoff level of 100 ug/mL was used for analysis. This was a secondary analysis of the Canadian Acetaminophen Overdose Study database (retrospective study).
Bottom line:
Table 2. Diagnostic accuracy of acetaminophen concentration obtained 2 to 4 hours post-ingestion to identify subsequent potentially toxic concentration measured 4 to 20 hours pos-ingestion.
|
| Subsequent 4-hour equivalent [APAP] | |
| [APAP] obtained 2 to 4 hours post-ingestion | >150 ug/mL | < 150 ug/mL |
| <10 | 0 | 89 |
| 10-20 | 2 | 79 |
| 20-50 | 6 | 209 |
| 50-100 | 19 | 249 |
| 100-150 | 46 | 253 |
| 150-200 | 161 | 195 |
| 200-300 | 276 | 46 |
| 300-450 | 148 | 5 |
| >450 | 38 | 0 |
Yarema MC, et al. Can a serum acetaminophen concentration obtained less than 4 hours post-ingestion determine which patients do not rquire treatment with acetylcysteine? Clin Toxicol 2016; online early: doi: 10.1080/15563650.2016.1247959
Category: Critical Care
Keywords: OHCA, ROSC (PubMed Search)
Posted: 12/6/2016 by Rory Spiegel, MD
(Updated: 2/8/2026)
Click here to contact Rory Spiegel, MD
The prognosis of patients who experienced OHCA, who have not achieved ROSC by the time they present to the Emergency Department, is dismal. As such, it behooves us as Emergency Physicians to identify the few patients with a potentially survivable event. Drennan et al examined the ROC data base and identified the cohort of patients who had not achieved ROSC and were transported to the hospital. The overall survival in this cohort was 2.0%. Factors that predicted survival were initial shockable rhythm and arrest witnessed by the EMS providers. Patients arriving to the ED without ROSC, that had neither of those prognostic factors had a survival rate of 0.7%.
Drennan IR, et al. A comparison of the universal TOR Guideline to the absence of prehospital ROSC and duration of resuscitation in predicting futility from out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. Resuscitation (2016)
Category: Visual Diagnosis
Posted: 12/5/2016 by Tu Carol Nguyen, DO
Click here to contact Tu Carol Nguyen, DO
27 year-old G2P1 presents with 3 days of abdominal pain that is mostly suprapubic. Denies any urinary symptoms and vaginal bleeding. Physical examination reveals slight rebound in the right lower quadrant.
An ultrasound revealed the following. What's the diagnosis?
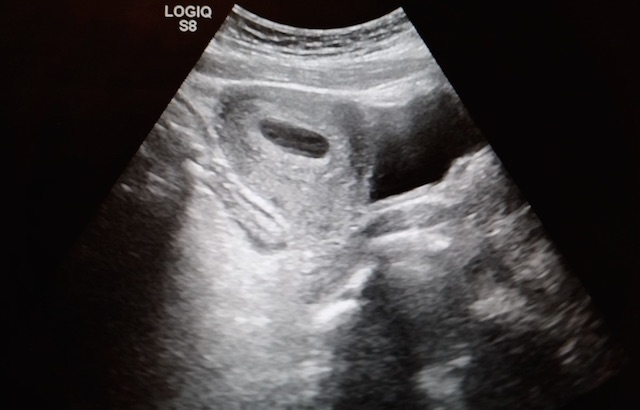
Pregnancy with Appendicitis
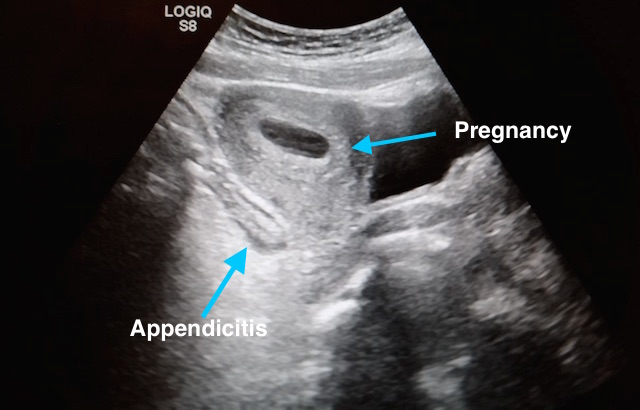
Take Home Points:
See previous pearl for how to conduct an ultrasound to evaluate for appendicitis.
Dewhurst C, Beddy P, Pedrosa I. MRI evaluation of acute appendicitis in pregnancy. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2013;37(3):566-75.
Israel GM, Malguria N, Mccarthy S, Copel J, Weinreb J. MRI vs. ultrasound for suspected appendicitis during pregnancy. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2008;28(2):428-33.
Segev L, Segev Y, Rayman S, Nissan A, Sadot E. The diagnostic performance of ultrasound for acute appendicitis in pregnant and young nonpregnant women: A case-control study. Int J Surg. 2016;34:81-85.
Segev L, Segev Y, Rayman S, Nissan A, Sadot E. Acute Appendicitis During Pregnancy: Different from the Nonpregnant State?. World J Surg. 2016.
Theilen LH, Mellnick VM, Longman RE, et al. Utility of magnetic resonance imaging for suspected appendicitis in pregnant women. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2015;212(3):345.e1-6.
Category: Pharmacology & Therapeutics
Keywords: esmolol, ventricular fibrillation, cardiac arrest (PubMed Search)
Posted: 11/21/2016 by Michelle Hines, PharmD
(Updated: 12/3/2016)
Click here to contact Michelle Hines, PharmD
Consider esmolol IV 500 mcg/kg loading dose followed by a continuous infusion of 0-100 mcg/kg/min for patients in refractory ventricular fibrillation
Follow me on Twitter @mEDPharmD
Category: Toxicology
Keywords: Drug Allergy, ADR, ADE (PubMed Search)
Posted: 12/1/2016 by Kathy Prybys, MD
(Updated: 12/2/2016)
Click here to contact Kathy Prybys, MD
Misclassification of adverse drug effects as allergy is commonly encountered in clinical practice and can lead to use of suboptimal alternate medications which are often less effective.
| DRUGS FREQUENTLY IMPLICATED IN ALLERGIC DRUG REACTIONS | ||
| Aspirin (other analgesics-antipyretics) | Sedative-hypnotics | Iodinated contrast media |
Understanding adverse drug reactions and drug allergies: principles, diagnosis and treatment aspects. Pourpak Z, et al. Recent Pat Inflamm Allergy Drug Discov. 2008 Jan;2(1):24-46.
Drug Allergy: An Updated Practice Parameter. Joint Task Force. Annals of Allergy, Asthma, & Immunology. Vol 105 ctober , 2010.
Antibiotic allergies in the medical record: effect on drug selection and assessment of validity. Lutomski,DM. Pharmacotherapy. 2008 Nov;28(11) 1348-53.
Category: International EM
Keywords: Zika, WHO, Public Health Emergency (PubMed Search)
Posted: 11/29/2016 by Jon Mark Hirshon, MPH, MD, PhD
(Updated: 11/30/2016)
Click here to contact Jon Mark Hirshon, MPH, MD, PhD
The World Health Organization announced on November 18th, 2016 that the Zika virus and associated consequences will no longer Public Health Emergency of International Concern. This changes the originally recommendation in February 2016.
However, Zika remains a “significant enduring public health challenge requiring intense action”. The consequences of the disease remains significant, especially for pregnant women and infants.
In early November, the CDC conducted a Clinical Outreach and Communication Activity (COCA) call on Zika in the ED: How Emergency Care Staff can Take Action. For more information, see: https://emergency.cdc.gov/coca/calls/2016/callinfo_110116.asp
https://emergency.cdc.gov/coca/calls/2016/callinfo_110116.asp
http://www.who.int/emergencies/zika-virus/en/
Category: Critical Care
Keywords: Pulmonary embolism, syncope (PubMed Search)
Posted: 11/29/2016 by Daniel Haase, MD
(Updated: 11/30/2016)
Click here to contact Daniel Haase, MD
--In this study, PE was diagnosed in ~17% of patients hospitalized for syncope (though this represents only ~4%% of patients presenting to the ED with syncope).
--Patients with PE were more likely to have tachypnea, tachycardia, relative hypotension, signs of DVT, and active cancer -- take a good history and do a good physical exam!
--Consider risk stratifying (Wells/Geneva) and/or performing a D-dimer (i.e "rule out" PE) on your syncope patients, particularly when no alternative diagnosis is apparent.
--The 17.3% prevalence of PE is in admitted patients only (in Italy). Again, 3.8% of patients presenting with syncope had PE diagnosed (though the study was not designed to study the prevalence of PE in patients presenting to the ED with syncope).
--Think about this! They only admitted 27.7% of patients with syncope!!! This suggests they only admitted sick patients with significant comorbidities.
--The vast majority of patients were ruled out by history, physical and ancillary testing and sent home (72.3%).
--Think about PE in syncope patients and do a reasonable work up (i.e. not all hospitalized PE patients need a CTA or V/Q)
Prevalence of Pulmonary Embolism among Patients Hospitalized for Syncope. Prandoni P, Lensing AW, et al. PESIT Investigators.. N Engl J Med. 2016 Oct 20;375(16):1524-1531
Category: Orthopedics
Keywords: Ankle Sprains (PubMed Search)
Posted: 11/26/2016 by Brian Corwell, MD
(Updated: 2/8/2026)
Click here to contact Brian Corwell, MD
Incidence and Cost of Ankle Sprains US Emergency Departments
In a sample of 225,114 ED patients with ankle sprains:
Lateral ankle sprains represent the vast majority of all ankle sprains (91%).
Lateral ankle sprains incur greater ED charges than medial sprains ($1008 vs. $914).
Lateral ankle sprains were more likely to have associated pain in the limb, sprain of the foot and abrasions of the hip/leg than medial sprains.
Medial sprains were more likely to include imaging.
Hospitalizations were more likely with high ankle sprains than lateral sprains.
There is a higher incidence of ankle sprains in younger patients (≤25 years) and in female patients (57%).
Shah et al., 2016. Incidence and Cost of Ankle Sprains in United States Emergency Departments. Sports Health Novemebr 2016.
Category: Pediatrics
Keywords: septic shock, cold shock, vasopressor, dopamine, epinephrine (PubMed Search)
Posted: 11/25/2016 by Mimi Lu, MD
Click here to contact Mimi Lu, MD
Which first-line vasoactive drug is the best choice for children with fluid-refractory septic shock? A prospective, randomized, blinded study of 120 children compared dopamine versus epinephrine in attempts to answer this debated question in the current guidelines for pediatric sepsis.
Bottom line: Dopamine was associated with an increased risk of death and healthcare–associated infection. Early administration of peripheral or intraosseous epinephrine was associated with increased survival in this population.
This was a small double-blind, prospective randomized controlled trial of 120 children with fluid-refractory septic shock in a PICU in Brazil. The primary outcome was to compare the effects of dopamine or epinephrine in severe sepsis on 28-day mortality; secondary outcomes were the rate of healthcare–associated infection, the need for other vasoactive drugs, and the multiple organ dysfunction score. Dopamine was associated with death (OR, 6.5; 95% CI, 1.1–37.8; p = 0.037) and healthcare–associated infection (odds ratio, 67.7; 95% CI, 5.0–910.8; p = 0.001). The use of epinephrine was associated with a survival odds ratio of 6.49. Further multicenter trials or single-center studeis are necessary to verify the reproducibiltiy of these results.
Ramaswamy KN, Singhi S, Jayashree M, Bansal A, Nallasamy K. Double-Blind Randomized Clinical Trial Comparing Dopamine and Epinephrine in Pediatric Fluid-Refractory Hypotensive Septic Shock.Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2016 Nov;17(11):e502-e512.
