Category: Orthopedics
Keywords: Lateral knee pain (PubMed Search)
Posted: 5/13/2017 by Brian Corwell, MD
Click here to contact Brian Corwell, MD
Iliotibial band tendonitis
IT band is the continuation of the tensor fascia lata and inserts on the tibia at Gerdy's tubercle
Common cause of lateral knee pain seen in Primary care/Sports med clinics
Mechanism: May be due to excessive friction between the IT band and the lateral femoral condyle
Second most common overuse injury of the knee (PF syndrome). Not an acute event.
Affects up to15% of active individuals
Impingement zone is at 30 degrees of knee flexion
Most common in runners and cyclists
Pain localized over the lateral femoral condyle. Better w/ rest. Often occurs at a predictable distance into the run and not at onset.
Exacerbated with changes to mileage or running terrain.
Additional risks include poor shoes (best to change every 300 to 500 miles), excessive foot pronation (pes planus), quad versus hamstring strength asymmetry, weak hip ABductors, leg length discrepancy, tight IT band.
Category: Neurology
Keywords: syncope, vasovagal, seizures, orthostatic, blood pressure (PubMed Search)
Posted: 5/10/2017 by Danya Khoujah, MBBS
Click here to contact Danya Khoujah, MBBS
Cheshire WP. Syncope. Continuum 2017;23(2):335–358.
Category: Orthopedics
Keywords: Lisfranc Fracture (PubMed Search)
Posted: 4/29/2017 by Michael Bond, MD
(Updated: 5/1/2017)
Click here to contact Michael Bond, MD
Lisfranc Fracture: Typically consists of a fracture of the base of the second metatarsal and dislocation, though it can also be associated with fractures of a cuboid.
Click below see image of fracture
Lisfranc Fracture:
Common current mechanism of injury is when a person steps into a hole and twists the foot. The original mechanism of injury that was described was when a horseman would fall of their horse with their foot still trapped in a stirrup.
Diagnosis should be considered if patient has difficultly weight bearing with pain on palpation over the 2nd and 3rdmetatarsals with an appropriate mechanism.

Category: Pediatrics
Keywords: analgesics, Ultram, (PubMed Search)
Posted: 4/28/2017 by Mimi Lu, MD
Click here to contact Mimi Lu, MD
Bottom line: Do not prescribe codeine or tramadol for cough or pain in children and breastfeeding moms.
A summary statement from the American Hospital Association (AHA) is posted below.
FDA RESTRICTS USE OF CODEINE AND TRAMADOL
MEDICINES IN CHILDREN, RECOMMENDS AGAINST USE IN BREASTFEEDING MOTHERS
The Issue:
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) today announced that it is restricting the use of codeine and tramadol medicines in children, as well as recommending against using codeine and tramadol medicines in breastfeeding mothers due to possible harm to their infants.
Codeine is approved to treat pain and cough, and tramadol is approved to treat pain. These medicines carry serious risks, including slowed or difficult breathing and death, which appear to be a greater risk in children younger than 12 years, and should not be used in these children. These medicines also should be limited in some older children.
The FDA is requiring several changes to the labels of all prescription medicines containing these drugs. These new actions further limit the use of these medicines beyond FDA's 2013 restriction of codeine use in children younger than 18 years to treat pain after surgery to remove the tonsils and/or adenoids. The agency is now adding:
The FDA is urging health care professionals and patients to report side effects involving codeine-and tramadol-containing medicines to the FDA MedWatch program, through its online form.
Category: Toxicology
Keywords: Dextromethorphan, Robotripping (PubMed Search)
Posted: 4/20/2017 by Kathy Prybys, MD
Click here to contact Kathy Prybys, MD

Dextromethorphan Abuse in Adolescence. Bryner JK, Wang K, et al. Archives of Pediatrics & Adolescent Medicine. 2006;160(12):1217-1222. doi:10.1001/archpedi.160.12.1217.
Dextromethorphan abuse. Antoniou T, Juurlink DN. CMAJ?: Canadian Medical Association Journal. 2014;186(16):E631. doi:10.1503/cmaj.131676.
Category: Pharmacology & Therapeutics
Posted: 4/27/2017 by Tu Carol Nguyen, DO
Click here to contact Tu Carol Nguyen, DO
Haloperidol has a higher D2 receptor antagonist effect than standard antiemetic treatment agents such as metoclopramide. In addition, newer antipsychotic agents such as Olanzapine have a high affinity at multiple antiemetic sites such as the dopamine and serotinergic receptors.
While formal RCT's are still in the works, multiple sources including palliative care, emergency medicine, and pain journals support their use in refractory emesis.
Consider Haloperidol 3-5 mg IV.
Check an EKG for long QTc prior to use. Consider dose reduction of haloperidol in those with hepatic impairment. Also consider dose reduction in patients taking carbamazepine, phenytoin, phenobarbital, rifampicin, or quinidine due to that pesky CYP3A4 inhibition.
Consider Olanzapine 2-5 mg IV.
Several case reports have shown a higher rate of success with olanzapine for refractory emesis. Olanzapine has similar precautions as those to haloperidol (EKG, hepatic impairment), although it's CYP drug interactions are less common. Additionally, use olanzapine cautiously in hyperglycemic patients as there are several case reports of olanzapine prompting episodes of DKA. Consider frequent blood sugar checks or small doses of insulin in hyperglycemic patients.
Take Home Points:
Consider the antipsychotic agents Haloperidol or Olanzapine for patients with refractory emesis, they may be more effective than traditional antiemetics.
Get an EKG prior to administration to check for QTc prolongation. As the classical and atypical antipsychotic agents are sedating, use caution in conjunction with other sedating medications (such as benzodiazepines).
Category: Neurology
Keywords: vasogenic cerebral edema, white matter, blood-brain-barrier, steroids (PubMed Search)
Posted: 4/26/2017 by WanTsu Wendy Chang, MD
Click here to contact WanTsu Wendy Chang, MD
Case image courtesy of Dr David Cuete, Radiopaedia.org, rID: 23178
Follow me on Twitter @EM_NCC!
Category: Critical Care
Posted: 4/25/2017 by Mike Winters, MBA, MD
(Updated: 2/7/2026)
Click here to contact Mike Winters, MBA, MD
Ventilator Settings for the Post-Arrest Patient
Jentzer JC, et al. Recent developments in the management of patients resuscitated from cardiac arrest. J Crit Care. 2017; 39:97-107.
Category: Orthopedics
Keywords: Hip, pediatrics, arthritis (PubMed Search)
Posted: 4/22/2017 by Brian Corwell, MD
(Updated: 2/7/2026)
Click here to contact Brian Corwell, MD
Septic Arthritis in Children
Classic presentation: Pain, fever (may not always be present)
Limited range of motion of joint or refusal to bear weight,
Joint swelling (difficult to visualize in hip or shoulder),
Limb held in position that allows greatest capsular volume (elbow held in 30° flexion for example)
Diagnostic testing may include diagnostic markers (ESR, CRP) or imaging (US/MRI)
Most common organisms: Staph and Strep, Neisseria (adolescents), HACEK organisms, consider gram negatives in immunocompromised children
DDX: Transient synovitis, osteonercrosis or osteomyelitis, Psoas abscess, acute leukemia, Lyme disease
A common ED presentation is the child with the painful limp
35% of all cases of septic arthritis
>50% of cases occur in children younger than 2yo
Hip held in flexion, Abduction, external rotation
Fever and inflammatory markers are more sensitive than WBC count and refusal to bear weight
Kocher criteria:
1) Refusal to weight bear on affected side
2) Sed rate greater than 40mm/hr
3) Fever (>38.5°C
4) WBC count of >12,000 mm3
IF
- 4/4 criteria are met, there is a 99.6% chance of septic arthritis;
- when 3/4 criteria are met, there is a 93% chance of septic arthritis;
- when 2/4 criteria are met, there is a 40% chance of septic arthritis;
- when 1/4 criteria are met, there is a 3% chance of septic arthritis;
CRP can also be incorporated into a diagnostic algorithm
CRP>2.0 (mg/dl) in a child who refuses to bear weight yields a 74% probability of septic arthritis
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10608376
Category: Pediatrics
Keywords: Bronchiolitis, asthma (PubMed Search)
Posted: 4/21/2017 by Jenny Guyther, MD
(Updated: 2/7/2026)
Click here to contact Jenny Guyther, MD
Predictive factors of asthma development in patients diagnosed with bronchiolitis include:
- Male sex (OR 1.3)
- Family history of asthma (OR 1.6)
- Age greater than 5 months at the time of bronchiolitis diagnosis (OR 1.4)
- More than 2 episodes of bronchiolitis (OR 2.4)
- Allergies (OR 1.6)
This was a retrospective study of 1991 children younger than 2 years that presented between 2000-2010 who were diagnosed with bronchiolitis. Primary care records were reviewed 1 year after their visit to the ED to see if the patient had a primary care diagnosis of asthma.
Of the initial study population, 817 patients had received a diagnosis of asthma at 1 year.
Since these patients were only followed up at 1 year, the amount of children who were later diagnosed with asthma may be underestimated.
Waseem et al. Factors Predicting Asthma in children with Acute Bronchiolitis. Pediatric Emergency Care. March 2017. Epub ahead of print.
Category: Toxicology
Keywords: lactic acidosis (PubMed Search)
Posted: 4/20/2017 by Hong Kim, MD
(Updated: 2/7/2026)
Click here to contact Hong Kim, MD
Lactic acids are often elevated in critical care patients (e.g. septic shock). It can be also elevated in setting of drug overdose or less frequently in therapeutic use due to interference of oxidative phosphorylation. Some of the agents include:
Bottom line:
Kraut JA, Madias NE. Lactic acidosis, N Engl J Med 2014;371:2309-19.
Category: International EM
Keywords: CDC, Shigella, antibiotic, health advisory (PubMed Search)
Posted: 4/19/2017 by Jon Mark Hirshon, MPH, MD, PhD
(Updated: 2/7/2026)
Click here to contact Jon Mark Hirshon, MPH, MD, PhD
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) just released an official health advisory through the Health Alert Network entitled: “CDC Recommendations for Diagnosing and Managing Shigella Strains with Possible Reduced Susceptibility to Ciprofloxacin”
Concerning treatment, one key point is:
Do not routinely prescribe antibiotic therapy for Shigella infection. Instead, reserve antibiotic therapy for patients for whom it is clinically indicated or when public health officials advise treatment in an outbreak setting.
o Shigellosis is generally a self-limited infection lasting 5-7 days.
o Unnecessary treatment with antibiotics promotes resistance.
o Treatment can shorten the duration of some illnesses, though typically only by 1-2 days
This Health Advisory describes the identification of emerging Shigella strains with elevated minimum inhibitory concentration values for ciprofloxacin and outlines new recommendations for clinical diagnosis, management, and reporting, as well as new recommendations for laboratories and public health officials. There are more details available on the website: https://emergency.cdc.gov/han/han00401.asp
RECOMMENDATIONS FOR CLINICIANS
Diagnosis
· Order stool culture for patients suspected of having a Shigella infection to obtain isolates for antimicrobial susceptibility testing.
· Order antimicrobial susceptibility testing when ordering stool culture for Shigella.
Management
· Do not routinely prescribe antibiotic therapy for Shigella infection. Instead, reserve antibiotic therapy for patients for whom it is clinically indicated or when public health officials advise treatment in an outbreak setting.
· When antibiotic treatment is indicated, tailor antibiotic choice to antimicrobial susceptibility results as soon as possible with special attention given to the MIC for fluoroquinolone antibiotics.
· Obtain follow-up stool cultures in shigellosis patients who have continued or worsening symptoms despite antibiotic therapy.
· Consult your local or state health department for guidance on when patients may return to childcare, school, or work.
· Counsel patients with active diarrhea on how they can prevent spreading the infection to others, regardless of whether antibiotic treatment is prescribed.
https://emergency.cdc.gov/han/han00401.asp
Category: Critical Care
Keywords: Central venous catheter, ultrasound (PubMed Search)
Posted: 4/18/2017 by Kami Windsor, MD
(Updated: 2/7/2026)
Click here to contact Kami Windsor, MD
Save time by using bedside ultrasound to confirm above-the-diaphragm central venous catheter (CVC) placement rather than waiting for chest x-ray confirmation:
1. Perform rapid push of saline (it doesn’t have to be agitated) through CVC while cardiac probe is placed with right atrium in view. Immediate visualization of bubbles (or “atrial swirl”) essentially confirms correct placement.
2. Perform the usual search for ipsilateral lung-sliding and the waves-on-the-beach to rule out procedural pneumothorax.
It makes sense that it’s going to be faster for you to use that internal jugular/subclavian central venous catheter (CVC) you just placed if you confirm with bedside ultrasound instead of waiting for the radiology tech to get the chest x-ray. But what’s the data?
Using pooled data from of 15 studies with 1553 CVC placements, Ablordeppey et al. found that ultrasound had a sensitivity of 86% and 98% specificity for detecting catheter malposition, with a positive likelihood ratio (LR) of 31.1 and a negative LR of 0.25. There was an almost 100% sensitivity and specificity for pneumothorax detection, and reduced confirmation time by 58 minutes.These findings are generally consistent across the board for the other studies out there.
1. Ablordeppey EA, Drewry AM, Beyer AB, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of central venous catheter confirmation by bedside ultrasound versus chest radiography in critically ill patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit Care Med. 2017; 45(4): 715-24.
2. Gekle R, Dubensky L, Haddad S, et al. Saline flush test: Can bedside sonography replace conventional radiography for confirmation of above-the-diaphragm central venous catheter placement? J Ultrasound Med. 2015;34(7):1295-9.
3. Weekes AJ, Johnson DA, Keller SM. Central vascular catheter placement evaluation using saline flush and bedside echocardiography. Acad Emerg Med. 2014; 21:65-72.
Category: Visual Diagnosis
Keywords: Pleural effusion; POCUS (PubMed Search)
Posted: 4/17/2017 by Tu Carol Nguyen, DO
Click here to contact Tu Carol Nguyen, DO
A 50 years old male with a history of CHF, presenting to the ED with progressively worsening shortness of breath. POCUS was performed. The picture shows the left lower part of the chest. What is the diagnosis?
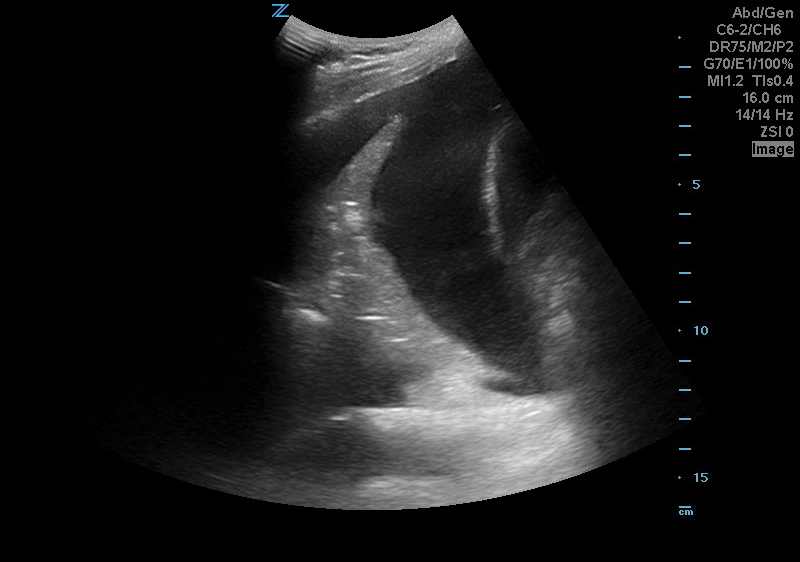
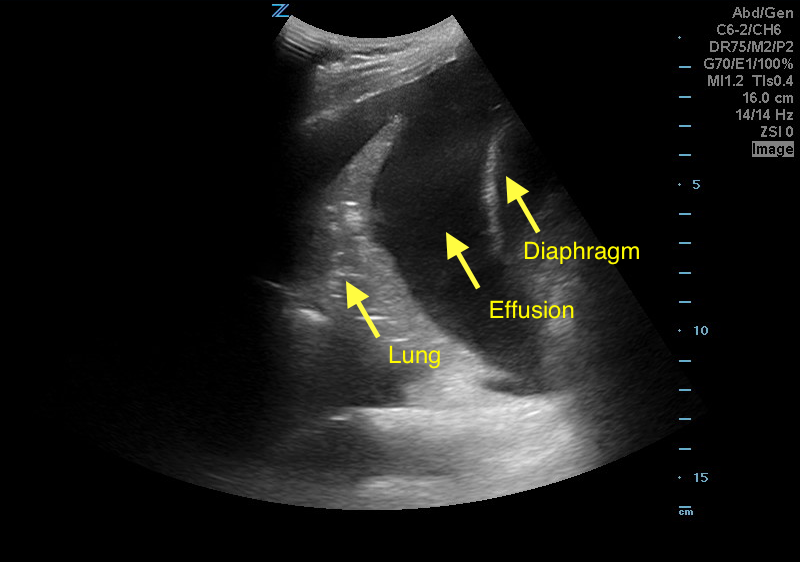
Answer: Pleural effusion
Eibenberger, K. L., Dock, W. I., Ammann, M. E., Dorffner, R., Hörmann, M. F., & Grabenwöger, F. (1994). Quantification of pleural effusions: sonography versus radiography. Radiology, 191(3), 681-684.
Atkinson, P., Milne, J., Loubani, O., & Verheul, G. (2012). The V-line: a sonographic aid for the confirmation of pleural fluid. Critical ultrasound journal, 4(1), 19.
Category: Orthopedics
Keywords: back pain, manipulation (PubMed Search)
Posted: 4/15/2017 by Michael Bond, MD
(Updated: 2/7/2026)
Click here to contact Michael Bond, MD
We all wish there was a great treatment regimen for our patients with back pain. However, most studies have shown that it really does not matter what you do, as most patients will get better in 6 weeks.
A recent study published in JAMA looked at the role of spinal manipulation to improve pain and function in adults with low back pain. They looked at 26 randomized controlled trails and found that there was modest benefit for spinal manipulation and it was similar to using NSAIDs.
So spinal manipulation may or may not work for some patients. Something to consider along with physical therapy if patients are not getting relief with home remedies.
Category: Pediatrics
Keywords: Pediatrics, urinary tract infection, urine concentration (PubMed Search)
Posted: 4/14/2017 by Jenny Guyther, MD
(Updated: 2/7/2026)
Click here to contact Jenny Guyther, MD
A recent study suggests that using a lower cut off value of white blood cells in dilute urine, may have a higher likelihood of detecting a urinary tract infection in children.
In dilute urine (specific gravity < 1.015), the optimal white blood cell cut off point was 3 WBC/hpf (Positive LR 9.9). With higher specific gravities, the optimal cut off was 6 WBC/hpf (Positive LR 10). Positive leukocyte esterase has a high likelihood ratio regardless of the urine concentration.
This was a retrospective study of 2700 infants < 3 months old who were evaluated for urinary tract infections (UTI). The UTI prevalence in this group was 7.8%. A UTI was defined as at least 50,000 colony forming units/mL from a catheterized specimen. Test characteristics looked at white blood cell and leukocyte esterase cut-offs, dichotomized into specific gravities: dilute (<1.015) and concentrated (>/=1.015).
Category: Neurology
Keywords: Glasgow Coma Scale, GCS, motor GCS, mGCS, Simplified Motor Scale, SMS (PubMed Search)
Posted: 4/12/2017 by WanTsu Wendy Chang, MD
Click here to contact WanTsu Wendy Chang, MD
Bottom Line: The motor GCS and Simplified Motor Scale (SMS) have similar discrimination when compared with the total GCS, and may be easier to use.
Chou R, Totten AM, Carney N, et al. Predictive Utility of the Total Glasgow Coma Scale Versus the Motor Component of the Glasgow Coma Scale for Identification of Patients with Serious Traumatic Injuries. Ann Emerg Med. 2017 Jan 11. [Epub ahead of print].
Follow me on Twitter @EM_NCC
Category: Critical Care
Keywords: Hyperoxia, Mechanical Ventilation (PubMed Search)
Posted: 4/11/2017 by Rory Spiegel, MD
(Updated: 2/7/2026)
Click here to contact Rory Spiegel, MD
The deleterious effects of hyperoxia are becoming more and more apparent. But obtaining a blood gas to ensure normoxia in a busy Emergency Department can be burdensome. And while the utilization of a non-invasive pulse oximeter seems ideal, the threshold that best limits the rate of hyperoxia is unclear.
Durlinger et al in a prospective observational study demonstrated that an oxygen saturation 95% or less effectively limited the number of patients with hyperoxia (PaO2 of greater than 100 mm Hg). Conversely when an SpO2 of 100% was maintained, 84% of the patients demonstrated a PaO2 of greater than 100 mm Hg.
Durlinger EM, Spoelstra-de man AM, Smit B, et al. Hyperoxia: At what level of SpO2 is a patient safe? A study in mechanically ventilated ICU patients. J Crit Care. 2017;
Category: Orthopedics
Keywords: EKG, athletes (PubMed Search)
Posted: 4/8/2017 by Brian Corwell, MD
(Updated: 2/7/2026)
Click here to contact Brian Corwell, MD
Most of our knowledge of the athlete’s EKG is based on white athletes.
African/Afro-Caribbean athletes are more likely to have an abnormal EKG than white athletes in multiple studies.
Different selective criteria have been developed to minimize classification of benign normal patterns as abnormal.
The 2010 ESC criteria classified 40.4% of black athletes as abnormal versus the Refined criteria which resulted in 11.5% of EKGs classified as abnormal.
This reduction was aided by the recognition that isolated anterior TWI in asymptomatic black athletes is considered a benign finding.
Note this does NOT apply if the TWI extend to the lateral leads
For example, T-wave inversion (TWI) was present in 23% of African/Afro-Caribbean athletes vs. 3.7% of white athletes (usually in contiguous anterior leads).
Other changes included a higher prevalence of early repolarization, RV hypertrophy, and LA/RA enlargement.
1) Jacob et al., 2016. Ethnic and Gender Specific Differences Among Athletes Participating in ECG Screening.
2 )WIlson et al., 2012. Significance of deep T-wave inversions in asymptomatic athletes with normal cardiovascular examinations: practical solutions for managing the diagnostic conundrum.
3) Brown et al., 2017. THe Complex Phentype of the Athlete's Heart: Implications for the Preparticipation Screening.
Category: Toxicology
Keywords: sodium bicarbonate, sodium acetate (PubMed Search)
Posted: 4/6/2017 by Hong Kim, MD
(Updated: 2/7/2026)
Click here to contact Hong Kim, MD
FDA announced a shortage of sodium bicarbonate on 3/01/17. Sodium bicarbonate is frequently used in acid-base disorder as well as in poisoning (cardiac toxicity from Na-channel blockade, e.g. TCA & bupropion, and salicylate poisoning).
Acetate is a conjugate base of acetic acid where acetate anion forms acetyl CoA and enters Kreb cycle after IV administration. Final metabolic products of acetate are CO2 and H2O, which are in equilibrium with bicarbonate via carbonic anhydrase activity.
Administration of sodium acetate increases the strong ion difference by net increase in cations, as acetate is metabolize, and leads to alkalemia.
Adverse events from sodium acetate infusion have been associated with its use as dialysate buffer: myocardial depression, hypotension, hypopnea leading to hypoxemia and hyperpyrexia. However, such adverse events have not been reported in toxicologic application.
Bottom line:
Sodium acetate can be administered safely in place of sodium bicarbonate if sodium bicarbonate is not available due to shortage.
Sodium acetate dose:
Neavyn MJ, Boyer EW, Bird SB, et al. Sodium acetate as a replacement for sodium bicarbonate in medical toxicology: a review. J Med Toxicol 2013;9:250-254.
