Category: Neurology
Keywords: stroke, tpa, ischemic stroke, acute stroke (PubMed Search)
Posted: 12/10/2008 by Aisha Liferidge, MD
(Updated: 2/7/2026)
Click here to contact Aisha Liferidge, MD
Important things to document in acute ischemic stroke cases from a medicolegal aspect:
-- time of onset
-- time of diagnosis
-- why tPA given or not given (the longer note for NOT giving it; 90% of related litigation cases based on NOT giving tPA.)
-- date and time on each side of note of every page
-- make it legible
Category: Vascular
Keywords: Hypertension, Epistaxis (PubMed Search)
Posted: 12/8/2008 by Rob Rogers, MD
(Updated: 2/7/2026)
Click here to contact Rob Rogers, MD
Hypertension and Epistaxis
We commonly encounter patients with epistaxis who are found to be hypertensive. Some have taught over the years that hypertension causes nosebleeds and that some nose bleeds won't stop until the BP is lowered...
Some pearls about HTN/Epistaxis:
Category: Cardiology
Keywords: hyperkalemia, treatment, management, beta agonists (PubMed Search)
Posted: 12/7/2008 by Amal Mattu, MD
(Updated: 2/7/2026)
Click here to contact Amal Mattu, MD
Category: Hematology/Oncology
Keywords: Thrombotic thrombocytopenia Purpura, TTP (PubMed Search)
Posted: 12/6/2008 by Michael Bond, MD
(Updated: 2/7/2026)
Click here to contact Michael Bond, MD
Just a quick remainder that Thrombotic thrombocytopenia Purpura, TTP, is typically described as a pentad of symptoms:
Not all symptoms need to be present and it would be rare for you to see the full pentad. Consider the diagnosis and request that the lab due a manual differentiation or blood smear. It is there that they will notice schistocytes, fragmented RBCs, that will help clinch the diagnosis.
Most cases of TTP are idiopathic (~60%) but secondary TTP is known to occur with cancer, pregnancy, HIV, bone marrow transplantation, immunospressive drugs like cyclosporin and tacrolimus, and platelet aggregation inhibitors such as cloperidol.
Treatment consists of plasmapheresis, plasma exchange, immunospression with steroids, Rituximab, and other chemotherapies.
Category: Toxicology
Keywords: carbon monoxide, CO, hyperbarics, HBO (PubMed Search)
Posted: 12/4/2008 by Ellen Lemkin, MD, PharmD
(Updated: 2/7/2026)
Click here to contact Ellen Lemkin, MD, PharmD
CO is formed from the incomplete combustion of carbon materials, eg. fires, stoves, portable heaters CO reversibly binds hemoglobin, producing carboxyhemoglobin (HbCO). This causes oxygen to bind more tightly to hemoglobin, releasing less in the tissues. Because of this, it affects the organs with the highest oxygen requirements most profoundly (eg. brain and heart).
Symptoms are mainly neurological and cardiovascular, but may include a wide variety of non-specific symptoms. The initial symptoms of CO poisoning may include headache and flu-like illness progressing to confusion, agitation, lethargy, seizures and coma.
Place patients on 100% oxygen to decrease the half-life of HbCO. Though controversial, HBO therapy is thought to decrease the incidence of neurologic sequelae. HBO therapy should be considered for patients with a HbCO level above 20%, severely symptomatic patients with lower levels, and pregnant patients. Remember that pulse oximetry will not be accurate.
-Poisondex
Category: Neurology
Keywords: fosphenytoin, phenytoin, dilantin, seizure (PubMed Search)
Posted: 12/3/2008 by Aisha Liferidge, MD
(Updated: 2/7/2026)
Click here to contact Aisha Liferidge, MD
** Fosphenytoin (Cerebyx) is a pro-drug of Phenytoin (Dilantin).
** Differences between fosphenytoin and phenytoin are primarily due to fosphenytoin being more water soluble.
Fosphenytoin versus Phenytoin:
• Fosphenytoin > less risk for cardiac-related adverse effects (propylene glycol not required for solubilization)
• Fosphenytoin > lower risk of local skin and subcutaneous irritation during infusion
• Fosphenytoin > can be given intramuscularly
• Fosphenytoin > can be infused at a faster rate (20 mg/kg phenytoin equivalents (PE’s) load at a rate of 100 to 150 mg of PE’s/minute) due to its safer side/adverse effects profile.
Category: Critical Care
Keywords: hemodialysis catheters (PubMed Search)
Posted: 12/2/2008 by Mike Winters, MBA, MD
(Updated: 2/7/2026)
Click here to contact Mike Winters, MBA, MD
Hemodialysis Catheters
Two weeks ago, we had a PEA arrest of a patient receiving HD. A significant delay occurred in administering fluids and medications as a result of "no iv access". Don't forget that in these situations you can use the hemodialysis catheter.
Category: Vascular
Keywords: Warfarin, Skin Necrosis (PubMed Search)
Posted: 12/1/2008 by Rob Rogers, MD
(Updated: 2/7/2026)
Click here to contact Rob Rogers, MD
Warfarin-Induced Skin Necrosis (WISN)
Some pearls about a rare, but serious side effect of Warfarin...
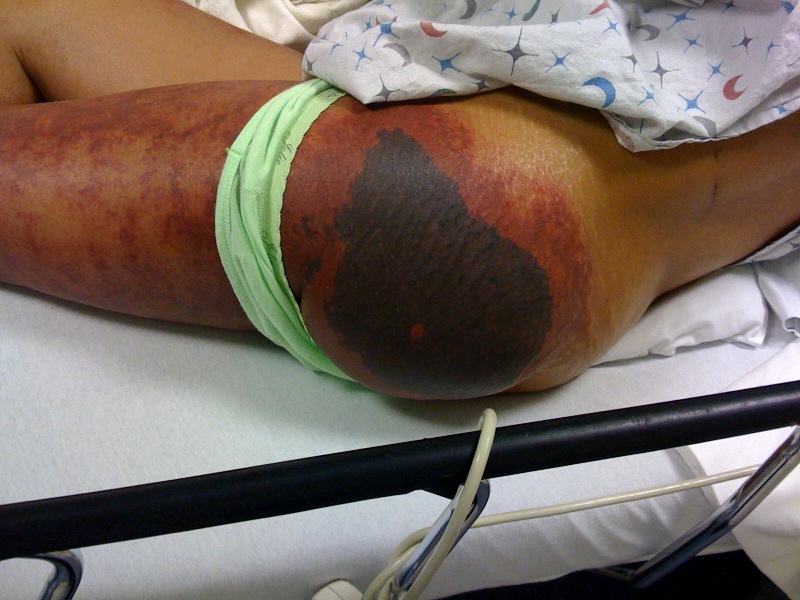
55 yo female presented to the ED on the day of hospital discharge for evaluation of this rash.
The rash began 4 days after starting Warfarin. Was being treated for a DVT.
Category: Cardiology
Keywords: hyperkalemia, treatment, management (PubMed Search)
Posted: 11/30/2008 by Amal Mattu, MD
(Updated: 2/7/2026)
Click here to contact Amal Mattu, MD
Category: Pediatrics
Keywords: SIDS (PubMed Search)
Posted: 11/28/2008 by Don Van Wie, DO
(Updated: 2/7/2026)
Click here to contact Don Van Wie, DO
SIDS
Sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS) is defined as the sudden death of an infant younger than 1 year that remains unexplained after a thorough case investigation, including the performance of a complete autopsy, examination of the scene of death, and review of the clinical history.
SIDS is the single most common cause of death in infants aged 1 mo to 1 yr
Education is key for prevention of these tragic events:
Following the "Back to Sleep" campaign, federal SIDS researchers have conducted annual surveys to examine how infant sleep practices and SIDS rates have changed. The rate of prone sleeping for infants decreased from approximately 75% in 1992 to a low of 11.3% in 2002
Since 1992, SIDS rates have fallen approximately 58%. In 2002, the National Center for Health Statistics reported a total of 2295 SIDS deaths nationwide for a SIDS rate in the United States of 0.51 per 1000 live births.
Bed-sharing may lead to compromise of the infants' airway because the infant may be suffocated by soft, loose bedding or a sleeping adult.
Cosleeping on a couch or sofa is associated with an unusually high risk for SIDS and should be avoided.
Category: Toxicology
Keywords: tryptophan (PubMed Search)
Posted: 11/28/2008 by Fermin Barrueto
(Updated: 2/7/2026)
Click here to contact Fermin Barrueto
Tryptophan - a precursor to melatonin, it is often blamed for the post prandial coma that many go into after a big turkey dinner. Never mind the 5000 kcals that was consumed during the meal. The supplement really doesn't help with sleeping. Interestingly, turkey isn't even in the top 10 or 20 of foods that contain tryptophan. The top five are:
1) Game meat (Elk): 746 mg of tryptophan
2) Seaweed (Spirulina): 736 mg of tryptophan
3) Spinach: 690 mg of tryptophan
4) Egg White: 673 mg of tryptophan
5) Soy protein: 630 mg of tryptophan
Supplements of L-tryptophan have been contaminated with a compound that has been associated with eosinophilia myalgia syndrome.
Category: Critical Care
Keywords: stress related mucosal injury, histamine antagonists, proton pump inhibitors, sucralfate (PubMed Search)
Posted: 11/25/2008 by Mike Winters, MBA, MD
(Updated: 2/7/2026)
Click here to contact Mike Winters, MBA, MD
Stress Related Mucosal Injury (SRMI)
Category: Vascular
Keywords: Hypertension (PubMed Search)
Posted: 11/24/2008 by Rob Rogers, MD
(Updated: 2/7/2026)
Click here to contact Rob Rogers, MD
What Hypertensive Patient Needs a Workup for End-Organ Damage?
Ah, the age old question...which hypertensive patients need an ED workup for end-organ damage? The "workup" for patients includes renal function, urinalysis, CXR, ECG, etc.
Some pearls regarding working patients up:
Category: Obstetrics & Gynecology
Posted: 11/23/2008 by Michael Bond, MD
(Updated: 2/7/2026)
Click here to contact Michael Bond, MD
Third Trimester Bleeding:
Category: Cardiology
Keywords: myocardial infarction, delirium, confusion (PubMed Search)
Posted: 11/23/2008 by Amal Mattu, MD
(Updated: 2/7/2026)
Click here to contact Amal Mattu, MD
Category: Toxicology
Keywords: cardiotoxicity, marcaine, bupivacaine (PubMed Search)
Posted: 11/20/2008 by Fermin Barrueto
(Updated: 2/7/2026)
Click here to contact Fermin Barrueto
Category: Neurology
Keywords: phenytoin, dilantin, seizure (PubMed Search)
Posted: 11/19/2008 by Aisha Liferidge, MD
(Updated: 2/7/2026)
Click here to contact Aisha Liferidge, MD
Category: Critical Care
Keywords: dopamine, hemodynamic medication, vasopressors (PubMed Search)
Posted: 11/18/2008 by Mike Winters, MBA, MD
(Updated: 2/7/2026)
Click here to contact Mike Winters, MBA, MD
Dopamine in the ED
Marino PL. Hemodynamic drugs. In: The Little ICU Book of Facts and Formulas. 2009 Ed. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia, PA.
Category: Infectious Disease
Keywords: Pneumonia (PubMed Search)
Posted: 11/18/2008 by Rob Rogers, MD
(Updated: 2/7/2026)
Click here to contact Rob Rogers, MD
Healthcare Associated Pneumonia (HCAP)....why is this important for the emergency physician?
Most of us are very familiar with the types of pneumonias commonly seen in clinical practice: community-acquired pneumonia (CAP), hospital-acquired pneumonia(HAP), and ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP). But, some may not be that aware of a relatively newer type of pneumonia that has been well-defined, healthcare-associated pnemonia (HCAP). Experts in infectious disease and critical care now say that we (the ED) should be assessing ALL pneumonia patients for HCAP risk factors.
Why care, you ask?
Risk factors: (most are common sense)
Treatment:
Category: Cardiology
Keywords: aortic dissection, aortic aneurysm, cardiac arrest, ultrasound (PubMed Search)
Posted: 11/16/2008 by Amal Mattu, MD
(Updated: 2/7/2026)
Click here to contact Amal Mattu, MD
Death from ruptured aortic aneurysms and thoracic aortic dissection has a few key features that often help in distinguishing these entities from other causes of rapid decompensation and sudden death:
1. These aortic disasters have a tendency to present with hypotension but without necessarily any specific complaints of pain (in contrast to common teaching).
2. These aortic disasters tend usually to produce PEA as the initial arrest rhythm.
3. These aortic disasters are often diagnosable on bedside ultrasound (AAA seen when scanning the abdomen; dissections frequently produce pericardial tamponade as they dissect backwards into the pericardial sack).
ALWAYS take a look at a patient's aorta and pericardium with the ultrasound when that patient presents in extremis or in cardiac arrest. The results can help make some critical diagnostic and therapeutic decisions.
[recent article related to this topic: Pierce LC, Courtney DM. Clinical characteristics of aortic aneurysm and dissection as a cause of sudden death in outpatients. Am J Emerg Med 2008;26:1042-1046.]
