Category: Orthopedics
Keywords: Scaphoid Fracture, CT (PubMed Search)
Posted: 10/17/2009 by Michael Bond, MD
(Updated: 2/8/2026)
Click here to contact Michael Bond, MD
Snuff Box Tenderness:
It has become the standard of care that individuals with snuff box tenderness, or pain with axial loading of the thumb, be placed in a thumb spica splint for 1-2 weeks until follow up x-rays can be done. This is done to rule out an occult scaphoid fracture. However, this practice can be hugely inconvenient to the patient and result in some atrophy of their forearm.
An alternative approach is to obtain a CT scan through the wrist to look specifically at the scaphoid bone. If the CT scan is negative you can send them home with some pain control, RICE (Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation) treatment and let them use thier thumb. No splint is needed. If it is positive then you can splint them and have them follow up with orthopedics or hand surgery.
Category: Toxicology
Keywords: partial agonist, buprenorphine (PubMed Search)
Posted: 10/15/2009 by Fermin Barrueto
Click here to contact Fermin Barrueto
This is a semi-synthetic opiate with partial agonist activity at the mu receptor. For an example of what a partial agonist is - see attached illustration. It is used in opioid addiction but is not as regulated as methadone clinics. Take a small course and you are licensed to prescribed it. Primary caregivers are now able to administer buprenorphine to assist addicts though it is not recommended if the patient is requiring more than 40mg of methadone (rules out everyone in Baltimore).
The tablets (Suboxone) also contain naloxone to prevent intravenous injection which would induce withdrawal. Naloxone is not orally bioavailable and thus can be mixed into the pill.
Overdose is treated like any other opioid and naloxone should work.
Buprenorphine can illicit an opioid withdrawal response if the patient is currently on an opioid and then takes buprenorphine.
Suppose to be safer than methadone - no QT prolongation and less respiratory depression
Category: Neurology
Keywords: pregnancy, seizure, epilepsy, first time seizure (PubMed Search)
Posted: 10/14/2009 by Aisha Liferidge, MD
(Updated: 2/8/2026)
Click here to contact Aisha Liferidge, MD
Category: Critical Care
Posted: 10/13/2009 by Mike Winters, MBA, MD
(Updated: 2/8/2026)
Click here to contact Mike Winters, MBA, MD
Critically Ill Patients with H1N1
Dominguez-Cherit G, Lapinsky SE, Macias AE, et al. Critically ill patients with 2009 influenza A (H1N1) in Mexico. JAMA (published online October 12, 2009) doi:10.1001/jama.2009. 1536.
Kumar A, Zarychanski R, Pinto R, et al. Canadian Critical Care Trials Group H1N1 Collaborative. Critically ill patients with 2009 influenza A (H1N1) infection in Canada. JAMA (published online October 12, 2009) doi:10.1001/jama.2009. 1496.
The Australia and New Zealand Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation (ANZ ECMO) influenza Investigators. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for 2009 influenza A (H1N1) acute respiratory distress syndrome. JAMA (published online October 12, 2009) doi.10.1001/jama.2009. 1535.
Category: Hematology/Oncology
Keywords: Thrombocytopenia (PubMed Search)
Posted: 10/12/2009 by Rob Rogers, MD
(Updated: 2/8/2026)
Click here to contact Rob Rogers, MD
Management of Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia (HIT)
HIT occurs when antibodies form to a Heparin-Platelet Factor 4 (PF4) complex in patients who have been exposed to Heparin.
The main clinical manifestation is thrombosis (arterial/venous). Treatment is unique in that only certain medications can be used.
Medical Management options in HIT:
So, when a patient with a history of HIT shows up in the ED with a DVT/PE or other thrombotic problem, these are your mainstay drugs.
Category: Cardiology
Keywords: troponin, non-cardiac (PubMed Search)
Posted: 10/11/2009 by Amal Mattu, MD
(Updated: 2/8/2026)
Click here to contact Amal Mattu, MD
The recent Baltimore City Marathon served as a nice reminder in a few cases that long-distance running and other ultra-endurance events can produce elevations in troponin levels. To review the non-cardiac-disease causes of troponin elevations:
sepsis, PE, COPD, carbon monoxide, intracranial abnormalities (including SAH, stroke, IC hemorrhage, seizures), ESRD, rhabdomyolysis, eclampsia and preeclampsia, extreme endurance exercises, UGI bleeding, LVH, catecholamine toxicity
Category: Misc
Keywords: Reimburshment, Coding (PubMed Search)
Posted: 10/7/2009 by Michael Bond, MD
(Updated: 2/8/2026)
Click here to contact Michael Bond, MD
Reimburshment Pearls:
Often charts are down coded as it is not clear from the documentation that your medical decision making was complex.
For instance, if your final diagnosis is GERD, and you do not document that you were also concerned about angina or a pneumothorax your level 5 chart could be coded as a level 3, since the final diganosis does not seem that complex. In order to prevent this document:
I realize that when you are busy this might be the last thing on your mind, but the difference between a level III chart and a level V chart is about $100, and the only additional work is the 3 minutes it would take to document what you did for the patient.
More to come...
Adapted from Michael A. Granovsky's ACEP lecture entitled :"RVU Killers: The Most Common Reimburshment Documentation Errors"
Category: Pediatrics
Keywords: nasal foreign bodies, button battery, batteries, ENT (PubMed Search)
Posted: 10/10/2009 by Adam Friedlander, MD
Click here to contact Adam Friedlander, MD
While it is often ok to defer removal of pesky nasal foreign bodies until ENT follow up, if the foreign body may be a button battery, emergent identification and removal is indicated.
Damage can occur in 3 hours, and by 24 hours, near complete necrosis of turbinates and ala has been described.
Dane S, Smally AJ, Peredy TR. A Truly Emergent Problem: Button Battery in the Nose. Academic Emergency Medicine. 2000; 7:204-206
Glynn F, Amin M, Kinsella J. Nasal Foreign Bodies in Children: Should They Have a Plain Radiograph in the Accident and Emergency? Pediatric Emergency Care. 2004;24:217-218.
Category: Toxicology
Keywords: haloperidol, cocaine, amphetamine, sympathomimetic (PubMed Search)
Posted: 10/8/2009 by Bryan Hayes, PharmD
(Updated: 2/8/2026)
Click here to contact Bryan Hayes, PharmD
A 34 y/o m presents to the ED agitated and combative with the following vitals signs: T 104.6, P 136, BP 198/124. His urine toxicology screen is positive for amphetamines.
Category: Neurology
Keywords: stroke, mca stroke (PubMed Search)
Posted: 10/7/2009 by Aisha Liferidge, MD
(Updated: 2/8/2026)
Click here to contact Aisha Liferidge, MD
Category: Critical Care
Posted: 10/6/2009 by Mike Winters, MBA, MD
(Updated: 2/8/2026)
Click here to contact Mike Winters, MBA, MD
Damage Control Resuscitation
Beekley, AC. Damage control resuscitation: A sensible approach to the exsanguinating surgical patient. Crit Care Med 2008;36:S267-74.
Category: Geriatrics
Keywords: erythrocyte sedimentation rate, sed rate, ESR (PubMed Search)
Posted: 10/4/2009 by Amal Mattu, MD
(Updated: 2/8/2026)
Click here to contact Amal Mattu, MD
Category: Gastrointestional
Keywords: PEG Tubes (PubMed Search)
Posted: 10/3/2009 by Michael Bond, MD
Click here to contact Michael Bond, MD
I am sure everybody has received a patient from a nursing home that had a malfunctioning PEG tube. Now if they would only crush the tablets before putting them down the tube, or better yet use liquid medications our life would be easier.
But what do you do if it is Friday and the GI lab is not open to Monday. The answer is that you can remove the PEG and replace it with another PEG tube or even a foley catheter will do for the weekend. The original PEG tube has a semi-rigid plastic ring (as shown in photo) and does not have a balloon that can be default. You can pull these out by placing counter traction on the abdominal wall and pulling with steady firm pressure. This may take a little more force than you are initially comfortable with.
Please see the attached photo of a PEG tube, and remember the other option is to admit these patients for IV fluids until the GI lab opens.
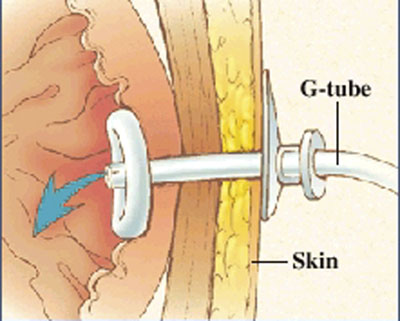
Photo taken from the Mount Littany Wellness library that can be accessed at http://www.mountnittany.org/wellness-library/healthsheets/documents?ID=6890
Category: Pediatrics
Keywords: pollutant, breastfeeding, environment, contaminants (PubMed Search)
Posted: 10/2/2009 by Heidi-Marie Kellock, MD
(Updated: 2/8/2026)
Click here to contact Heidi-Marie Kellock, MD
While breastfeeding is still the preferred source of infant nutrition by the AAP, a little-known fact is that breastfeeding may expose the nursing infant to environmental pollutants to which they might not normally be exposed. If you have a mother that appears ill due to exposure to any of these agents, don't forget to have the infant examined as well for signs of intoxication.
American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Environmental Health. Chapter 3. In: Etzel RA, ed. Pediatric Environmental Health, 2nd ed. Elk Grove Village, IL: American Academy of Pediatrics; 2003.
Category: Neurology
Keywords: status epilepticus, seizure, phenytoin, phenobarbital, high dose phenytoin (PubMed Search)
Posted: 9/30/2009 by Aisha Liferidge, MD
(Updated: 2/8/2026)
Click here to contact Aisha Liferidge, MD
Category: Cardiology
Keywords: Acute MI, papillary muscle rupture (PubMed Search)
Posted: 9/29/2009 by Rob Rogers, MD
(Updated: 2/8/2026)
Click here to contact Rob Rogers, MD
Severe mitral regurgitation (MR) after MI, accompanied by cardiogenic shock carries a poor prognosis.
Severe MR in many cases is due to infarction of the posterior papillary muscle, and in these cases the area of infarction tends to be less extensive than in those with MR due to severe left ventricular dysfunction.
Take Home Pearl:
The presence of pulmonary edema and/or cardiogenic shock in a patient with an inferior STEMI should prompt consideration for acute MR due to papilary muscle rupture. Get an echo as fast as you can to confirm or r/o the diagnosis. Treatment is afterload reduction, inotropic support, and urgent surgical repair.
Category: Cardiology
Keywords: pheochromocytoma, hypertension (PubMed Search)
Posted: 9/27/2009 by Amal Mattu, MD
(Updated: 2/8/2026)
Click here to contact Amal Mattu, MD
Don't forget about pheochromocytoma as a possible cause of severe hypertension...especially in those patients that are recalcitrant to "normal" medications. A few important points:
1. Incidence may be as high as 0.2% of patients with hypertension...sounds very rare, but statistically we'll all see some during our career.
2. Mortality may be as high as 10% if unrecognized; but if recognized and treated, excellent prognosis.
3. Suspect this in patients with intermittent episodes of flushing, palpitations, diaphoresis, headaches, and hypertension.
4. Treatment with beta blockers alone (including labetalol) may induce unopposed alpha-activity and worsen BP.
5. Treat with nitroprusside or phentolamine (an alpha blocker). Phentolamine is 5 mg IV, can be repeated every 5-10min as needed.
6. After phentolamine is given, there may be reflex tachycardia. NOW you can add beta blockers.
The most important thing is to keep the diagnosis in mind. It's out there! But you'll miss 100% of the diagnoses you don't consider.
Category: Orthopedics
Keywords: AC Joint, Separation, Dislocation (PubMed Search)
Posted: 9/26/2009 by Michael Bond, MD
(Updated: 2/8/2026)
Click here to contact Michael Bond, MD
AC Joint Dislocations
The acromioclavicular (AC) Joint is commonly injured when a person falls onto their shoulder.
The AC Joint consists of three ligaments:
Injuries to this joint are classified as Type I – Type VI and involve sprain or tears of the AC or CC ligaments
Category: Pediatrics
Posted: 9/25/2009 by Rose Chasm, MD
(Updated: 9/26/2009)
Click here to contact Rose Chasm, MD
Rimoin DL, Connor JM, Pyeritz RE, eds. Emergy adn Rimoin's Principles and Practice of Medical Genetics. 4th ed. New York, NY: Churchill Livingstone; 2002
Ryan S, Scriver CR. Phenylalanine hydroxylase deficiency. GeneReviews. Seattle, Wash: Children's Health System and University of Washington; 2003.
Category: Toxicology
Keywords: atypical antipsychotic, aripiprazole (PubMed Search)
Posted: 9/24/2009 by Fermin Barrueto
(Updated: 2/8/2026)
Click here to contact Fermin Barrueto
Aripiprazole (Abilify): a new atypical antipsychotic partially agonizes D2 and serotonin receptors though its compelte mechanism is not known. Used in schizophrenia, in overdose you may see the following symptoms (from a retrospective study done over 4 years worth of calls to a PCC):
The study was with over 255 patients. Though QT prolongation is listed, it is not common with this medication.
Young MC, et al. Risk assessment of isolated aripiprazole exposures and toxicities: a retrospective study. Clin Tox 2009; 47(6): 580-3.
