Category: Visual Diagnosis
Posted: 11/5/2012 by Haney Mallemat, MD
Click here to contact Haney Mallemat, MD
11 year-old male is tackled and falls on his outstretched hand while playing football. X-rays are shown below. What's the diagnosis?
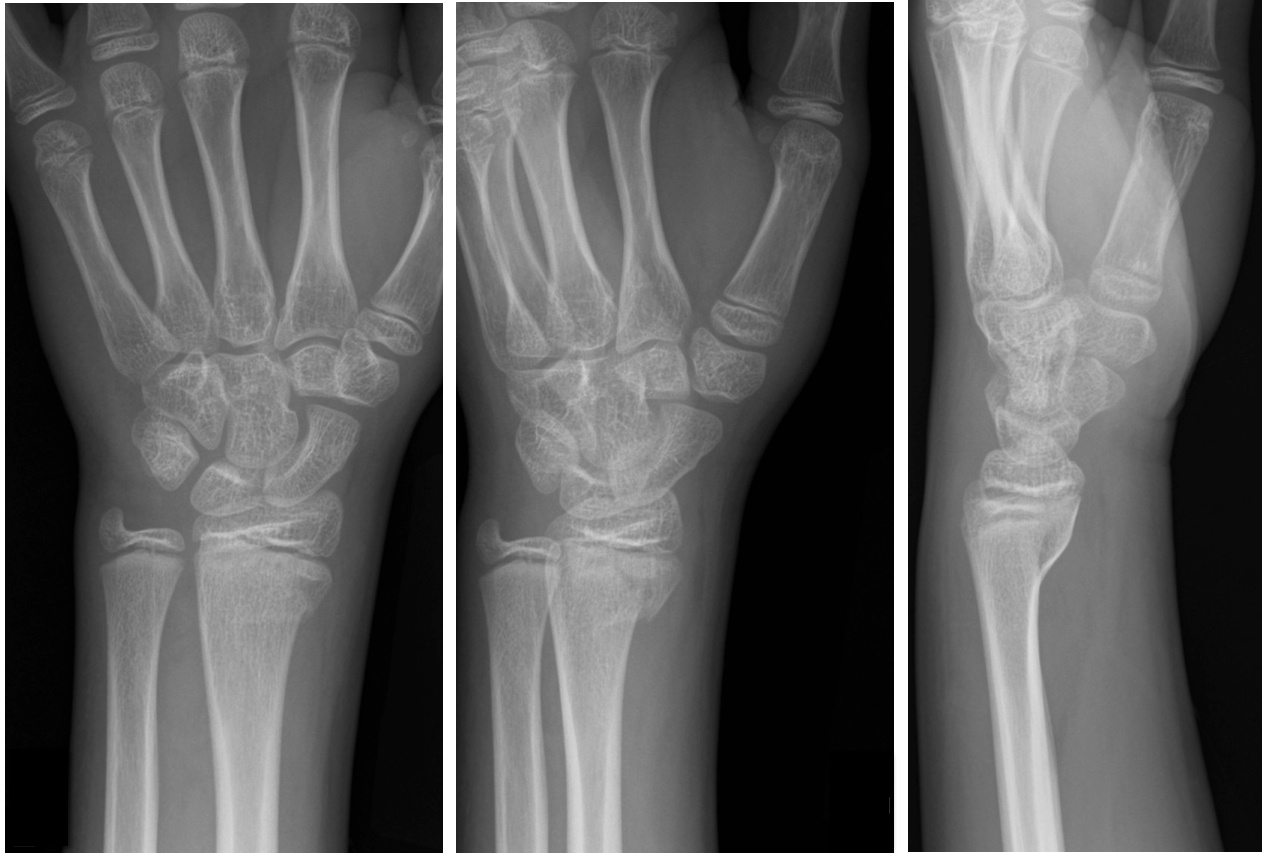
Answer: Salter-Harris Fracture - Type II
Salter-Harris Fracture (SHF)
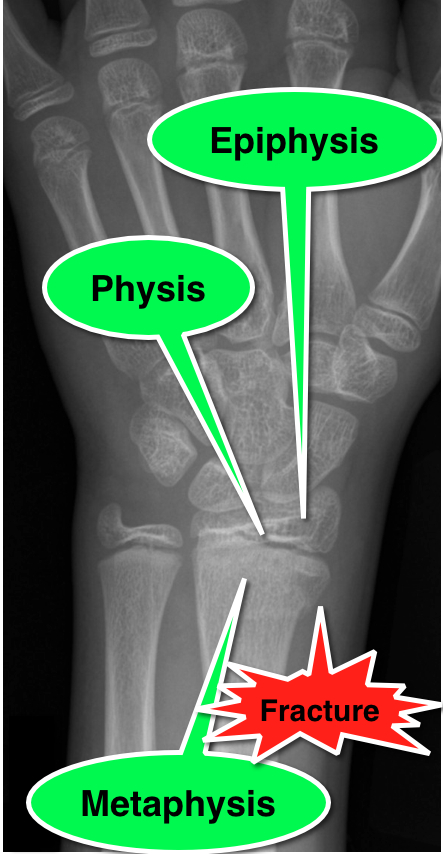
SHF are fractures through the growth plate (a.k.a. the physis), therefore are unique to pediatric patients.
Fractures are categorized according to involvement of the physis, metaphysis, and epiphysis. Proper injury classification is important because it affects both the treatment and potential long-term complications. Radiographic findings can sometimes be subtle; especially Type 1 SHF.
Occult SHF should be suspected when there is tenderness or swelling over an epiphyseal surface with X-rays negative for fracture. In this case, children should be splinted and urgently followed up.
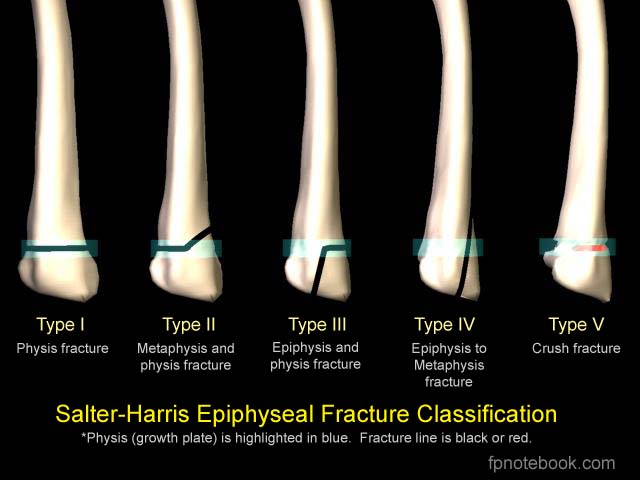
SHF classification
Bonus Pearl:
Use mnemonic SALTR to remember fracture type (Type I-Slipped, II-Above physis, III-Lower physis, IV-Through physis, V-Rammed)
emedicine.medscape.com/article/412956-overview
Salter, R and Harris R. Injuries involving the Epiphyseal Plate. Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery. Vol 45-A. Issue 3, April 1963.
fpnotebook.com/_media/OrthoFractureSalterHarris.jpg
Follow me on Twitter (@criticalcarenow) or Google+ (+haney mallemat)
