Category: Orthopedics
Keywords: Compartment Syndrome (PubMed Search)
Posted: 11/16/2013 by Michael Bond, MD
(Updated: 2/8/2026)
Click here to contact Michael Bond, MD
Compartment Syndrome
Compartment syndrome is classically described as having the 6 Ps:
The diagnosis of compartment syndrome can be difficult but ultimately it comes down to measuring the pressures in the area of concern. Various recommendations of the allowed pressure can be found, but in general a fasciotomy is not needed if the compartment pressure is 30 mmHg less then the diastolic pressure (The Delta 30). So if the patients diastolic pressure is 70, a fasciotomy is not need if the compartment pressure is less then 40.
Finally, if you are suspecting compartment pressure do NOT elevate the limb. Leave it in a dependent position to help improve blood flow into the limb.
Category: Orthopedics
Keywords: back pain, cauda equina (PubMed Search)
Posted: 11/4/2013 by Brian Corwell, MD
(Updated: 11/9/2013)
Click here to contact Brian Corwell, MD
Cauda equina syndrome results from compression of multiple lumbar and sacral nerve roots
Causes: Central disc herniation, spinal epidural abscess, malignancy, trauma, hematoma.
Consider this entity in those with back pain and radiculopathy at multiple spinal levels
Urinary retention occurs in >90% of patients
Saddle anesthesia occurs in 75%
Decreased rectal sphincter tone occurs in 60 to 80%
A post void residual volume <100 mL makes this entity very unlikely
Category: Orthopedics
Keywords: gluteus, trendelenberg test, hip pain (PubMed Search)
Posted: 10/26/2013 by Brian Corwell, MD
(Updated: 2/8/2026)
Click here to contact Brian Corwell, MD
Lateral hip pain
Findings of weakness and/or pain while testing hip abduction may point to gluteus medius muscle dysfunction with associated with greater trochanteric pain syndrome.
The Trendelenburg test may help. The patient stands on the affected leg. A negative test result occurs when the pelvis rises on the opposite side. A positive test result occurs when the pelvis on the opposite side drops and indicates a weak or painful gluteus medius muscle.
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=TY-G4ErruUA
Category: Orthopedics
Keywords: Stress fractures, runners (PubMed Search)
Posted: 9/28/2013 by Brian Corwell, MD
Click here to contact Brian Corwell, MD
Prior fracture represents the strongest predictor of stress fracture in both sexes
For girls: Low body mass index, (<19), late menarche (age 15 or older), previous participation in gymnastics and dance.
For boys: increased number of seasons.
Participation in basketball appears protective in boys.
This may represent a modifiable risk factor for stress fractures.
Tenforde AS, Sayres, LC, et al. Identifying sex-specific risk factors for stress fractures in Adolescent Runners. 2013
Category: Orthopedics
Keywords: Basilar joint, thumb, arthritis, Basal joint grind test (PubMed Search)
Posted: 9/14/2013 by Brian Corwell, MD
Click here to contact Brian Corwell, MD
The thumb MCP joint is subject to arthritric changes.
Sx's of arthritis will frequently present with pain in a similar region to deQuervain's disease.
The basal joint grind test
Perform by stabilizing the triquetrum with your thumb and index finger and then dorsally subluxing the thumb metacarpal on the trapezium while providing compressive force with the opposite hand.
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=oEJH7KFGx_Y
Category: Orthopedics
Keywords: Charcot Joints (PubMed Search)
Posted: 8/17/2013 by Michael Bond, MD
Click here to contact Michael Bond, MD
Charcot Joint - Neuropathic arthropathy
A Charcot Joint is a progressive degeneration of a weight bearing joint that is normally seen in patients that have decreased peripheral sensation and proprioception.
Conditions associated with Charcot Joints are:
• Alcohol neuropathy
• Cerebral palsy
• Diabetes mellitus
• Spinal Cord Injury
• Strokes
• Syphilis (tabes dorsalis)
The foot is most commonly affected and radiographs can also show bony destruction, bone resorption, and gross deformity. The onset of pain and deformity is typically insidious. Charcot joints are often associated with ulcerations, secondary osteomyelitis, and can lead to amputations.


It is important to recognize the presence of a Charcot Joint so that the patient can be referred to Orthopaedics and treated (often with cast immobilization) to prevent further destruction of the joint.
Category: Orthopedics
Keywords: Trigger finger, flexor tendon, locked finger (PubMed Search)
Posted: 8/8/2013 by Brian Corwell, MD
(Updated: 2/8/2026)
Click here to contact Brian Corwell, MD
The flexor tendons of the finger may become thickened and narrowed from chronic inflammation and irritation.
- Causes limitation in range of motion and snapping or locking during flexion
- Can involve any digit but usually the ring and the long finger
CC: pain, "catching" May awake to finger being "locked" with spontaneous resolution during the day
Stenosis occurs at the MCP level
PE: Distal flexor crease tender to palpation and may have a painful nodule
Full finger flexion is sometimes not possible
Tx: NSAIDs and steroid injection in tendon sheath. If this fails - surgical release.
Category: Orthopedics
Keywords: Hand nodules, contactures (PubMed Search)
Posted: 7/28/2013 by Brian Corwell, MD
(Updated: 2/8/2026)
Click here to contact Brian Corwell, MD
Dupuytren disease is a nodular thickening and resultant contraction of the palmer fascia.
Increased in those of Northern European dissent.
One or more painful nodules located near the distal palmer crease.
Over time may result in flexion at the MCP joint.
Most commonly affects the ring finger.
Sensation is normal.
Over time affects ADLs
Tx: night splints and surgery
Category: Orthopedics
Keywords: ulnar nerve, entrapment (PubMed Search)
Posted: 7/13/2013 by Brian Corwell, MD
(Updated: 2/8/2026)
Click here to contact Brian Corwell, MD
Tests for distal ulnar nerve entrapment
Ask patient to hold a piece of paper between the thumb and the index finger
Normally this is a fairly simple task.
With an unlar nerve palsy, the patient will substitute with the FPL (flexor pollicis longus - median nerve innervation). This causes flexion of the thumb in order to maintain the grip since the adductor pollicis cannot be used. This causes thumb flexion rather than extension.
http://www.mims.com/resources/drugs/common/CP0042.gif
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yJTIhm1VfSI
Category: Orthopedics
Posted: 6/29/2013 by Michael Bond, MD
(Updated: 2/8/2026)
Click here to contact Michael Bond, MD
Sternal fractures
Brookes JG, Dunn RJ, Rogers IR. Sternal fractures: a retrospective analysis of 272 cases. J Trauma. Jul 1993;35(1):46-54. PMID 8331712
Category: Orthopedics
Keywords: Tennis Elbow, ECRB tendon (PubMed Search)
Posted: 6/22/2013 by Brian Corwell, MD
Click here to contact Brian Corwell, MD
Tennis Elbow
The tendon usually involved in tennis elbow is called the Extensor Carpi Radialis Brevis (ECRB).
The ECRB muscle helps stabilize the wrist when the elbow is straight.
Ask the patient to straighten the arm at the elbow and then perform resisted long finger extension. This will stress the ECRB and reproduce the pain. One can also ask the patient to lift the top of a chair in the air with the elbow extended.
Category: Orthopedics
Keywords: Trapezium, Fracture (PubMed Search)
Posted: 6/15/2013 by Michael Bond, MD
Click here to contact Michael Bond, MD
Trapezium Fractures
Suspect the Diagnosis when you note
If you are suspected the diagnosis oblique radiographs or a CT scan of the wrist will note the fracture the best.
Treatment consists of placing the patient in a thumb spica splint.
Category: Orthopedics
Keywords: Concussion, Adolscents (PubMed Search)
Posted: 6/8/2013 by Brian Corwell, MD
(Updated: 6/9/2013)
Click here to contact Brian Corwell, MD
The adolescent brain has not yet reached full maturation and is in a period of rapid development from ages 14 - 16.
Adolescents have been found to be more sensitive to the effects of concussion than adults
Concussed adolescents have deficits in attention and executive function lasting up to 2 months post injury.
Be aware that the adolescent brain will require extended recuperation time following injury
In the future, discharge instructions might need to say more than "don't get hit in the head till your headache goes away." Because of deficits in attention and executive function, physicians should consider recommendations about adolescents and jobs, school work and driving an automobile.
Effects of concussion on attention and executive function in adolescents. Howell D, Osternig L, et al. Medicine & Sceince in Sports and Exercise. June 2013
Category: Orthopedics
Keywords: Frozen shoulder, adhesive capsulitis (PubMed Search)
Posted: 5/25/2013 by Brian Corwell, MD
(Updated: 2/8/2026)
Click here to contact Brian Corwell, MD
Adhesive capsulitis aka frozen shoulder
idiopathic loss of BOTH active and passive motion (this is a significant reduction of at least 50%)
Motion is stiff and painful especially at the extremes
Occurs due to thickening and contracture of the shoulder capsule
Affects patients between the ages of 40 and 60
Diabetes is the most common risk factor
Imaging is normal and only helpful to rule out other entities such as osteophytes, loose bodies etc.
Treatment includes NSAIDs, moist heat and physical therapy.
Patients should expect a recovery period of 1-2 years!
Category: Orthopedics
Keywords: Fabella (PubMed Search)
Posted: 5/18/2013 by Michael Bond, MD
(Updated: 2/8/2026)
Click here to contact Michael Bond, MD
Fabella Syndrome
The fabella is a sesamoid bone that is embedded in the tendon of the gastrocnemius muscle where the fibers of the popliteus, arcuate complex and the fibular-fabellar ligament attach.
Fabella syndrome is a painful condition of the posterolateral knee that is exacerbated when the knee is extended. The pain can be exacerbated by palpation of the fabella and if it is compressed against the condyles. The condition is most common in adolescence, but occurs in adults too.
Consider this condition in patients with posterolateral knee pain, which can also be due to tears of the posterior horn of the lateral meniscus, and tendonitis of the lateral head of the gastrocnemius.
Category: Orthopedics
Keywords: MRI, spinal cord compression (PubMed Search)
Posted: 4/27/2013 by Brian Corwell, MD
Click here to contact Brian Corwell, MD
You have a patient with a spinal cord syndrome and you order the MRI. Have you ever had that conversation with radiology where you have to "choose" what part of the spine you want imaged?
The entire spine needs to be imaged!
The reason: False localizing sensory levels.
For example: The patient has a thoracic sensory level that is caused by a cervical lesion.
A study of 324 episodes of malignant spinal cord compression (MSCC) found that clinical signs were very unreliable indicators of the level of compression. Only 53 patients (16%) had a sensory level that was within 3 vertebral levels of the level of compression demonstrated on MRI.
Further, pain (both midline back pain and radicular pain) was also a poor predictor of the level of compression.
Finally, of the 187 patients who had plain radiographs at the level of compression at referral, 60 showed vertebral collapse suggesting cord compression, but only 39 of these predicted the correct level of compression (i.e. only 20% of all radiographs correctly identified the level of compression).
The authors note that frequently only the lumbar spine was XR at the time of clinical presentation (usually at the referring hospital), presumably due to false localizing signs and a low awareness on the part of clinicians that most MSCC occurs in the thoracic spine (68% in this series).
Summers D, et al. Assessment of MSCC using MRI Br J Radiol 2001;74:977-8.
Category: Orthopedics
Keywords: MRI, spinal cord compression (PubMed Search)
Posted: 4/13/2013 by Brian Corwell, MD
Click here to contact Brian Corwell, MD
You have a patient with a spinal cord syndrome and you order the MRI. Have you ever had that conversation with radiology where you have to "choose" what part of the spine you want imaged?
The entire spine needs to be imaged!
The reason: False localizing sensory levels.
For example: The patient has a thoracic sensory level that is caused by a cervical lesion.
A study of 324 episodes of malignant spinal cord compression (MSCC) found that clinical signs were very unreliable indicators of the level of compression. Only 53 patients (16%) had a sensory level that was within 3 vertebral levels of the level of compression demonstrated on MRI.
Further, pain (both midline back pain and radicular pain) was also a poor predictor of the level of compression.
Finally, of the 187 patients who had plain radiographs at the level of compression at referral, 60 showed vertebral collapse suggesting cord compression, but only 39 of these predicted the correct level of compression (i.e. only 20% of all radiographs correctly identified the level of compression).
The authors note that frequently only the lumbar spine was XR at the time of clinical presentation (usually at the referring hospital), presumably due to false localizing signs and a low awareness on the part of clinicians that most MSCC occurs in the thoracic spine (68% in this series).
Summers D, et al. Assessment of MSCC using MRI Br J Radiol 2001;74:977-8.
Category: Orthopedics
Keywords: Ottawa, Knee, Pittsburgh (PubMed Search)
Posted: 3/30/2013 by Michael Bond, MD
Click here to contact Michael Bond, MD
Knee Pain Injuries are Radiographs needed?
Many people know that the folks in Ottawa have come up with a rule to determine whether radiographs are needed in patients complaining of knee pain. The Ottawa Knee rules that that radiographs are only required for knee injuries with any of the following:
• Age 55 years or older
• isolated tenderness of patella
• tenderness at head of fibula
• inability to flex to 90'
• inability to bear weight both immediately and in the emergency department (4 steps)
Well another group in Pittsburgh have their own set of rules that were recently shown to be more specific with equal sensitivity. The Pittsburgh decision rules state that radiographs are only needed if
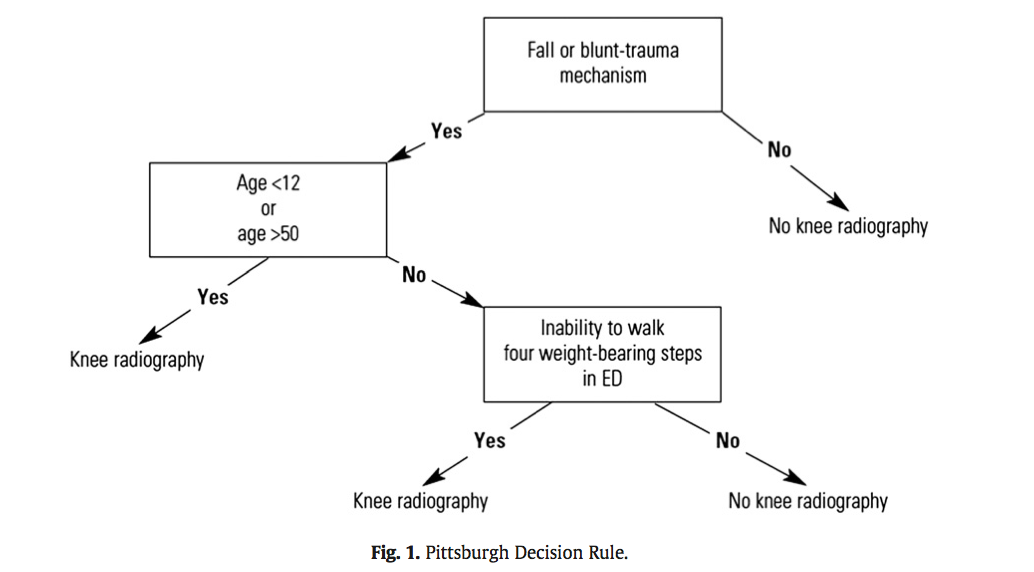
So consider using the Pittsburgh or Ottawa Knee rules the next time you have a patient with knee pain to determine if those radiographs are really needed.
The full article can be found at http://www.ajemjournal.com/article/S0735-6757%2812%2900566-9/abstract
Cheung TC, Tank Y, Breederveld RS, Tuinebreijer WE, de Lange-de Klerk ESM, MD RJD. Diagnostic accuracy and reproducibility of the Ottawa Knee Rule vs the Pittsburgh Decision Rule. Am J Emerg Med. Elsevier Inc; 2013 Feb 1;:1–5.
Category: Orthopedics
Keywords: scapular, fracture (PubMed Search)
Posted: 3/16/2013 by Michael Bond, MD
(Updated: 2/8/2026)
Click here to contact Michael Bond, MD
Scapular fractures
Carol Rivers Written Board Review Book 7th edition, Ohio Acep
Category: Orthopedics
Keywords: Concussion, closed head injury, return to play (PubMed Search)
Posted: 3/9/2013 by Brian Corwell, MD
Click here to contact Brian Corwell, MD
Key components in the determination of return to play following concussion include assessment of 1) brain function, 2) reaction time and 3) balance testing
Balance testing has become increasingly utilized in the diagnosis and management of sports related concussion. Studies have identified temporary or permanent deficits in static and/or dynamic balance in individuals with mild-to-moderate traumatic brain injury and sports related concussion. An example of this is the Balance Error Scoring System (BESS). Three stances are testing (narrow double-leg stance, single leg stance and a tandem stance) with the hands on the hips and eyes closed for 20 seconds. The FNL Sideline Concussion Assessment Tool utilizes a modified BESS. Example video below:
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xtJgv-D7IdU
