Category: Visual Diagnosis
Posted: 10/25/2016 by Tu Carol Nguyen, DO
(Updated: 10/26/2016)
Click here to contact Tu Carol Nguyen, DO
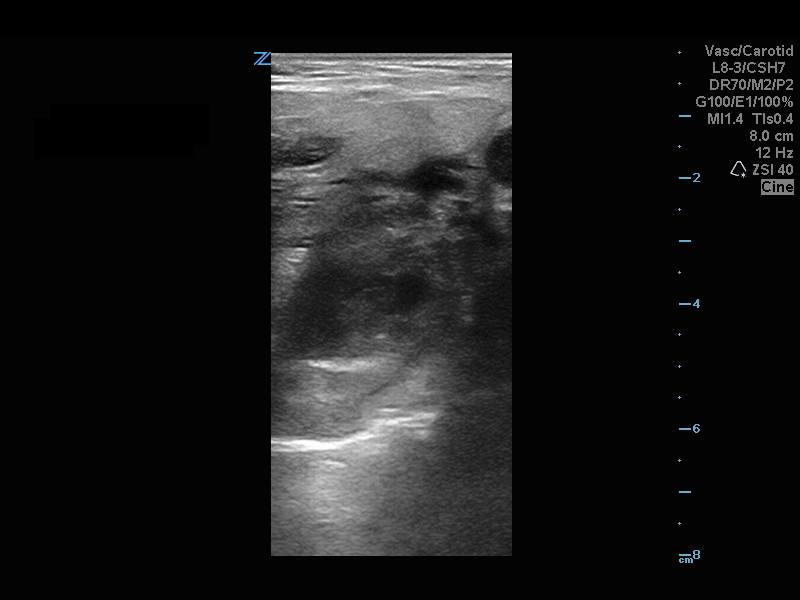
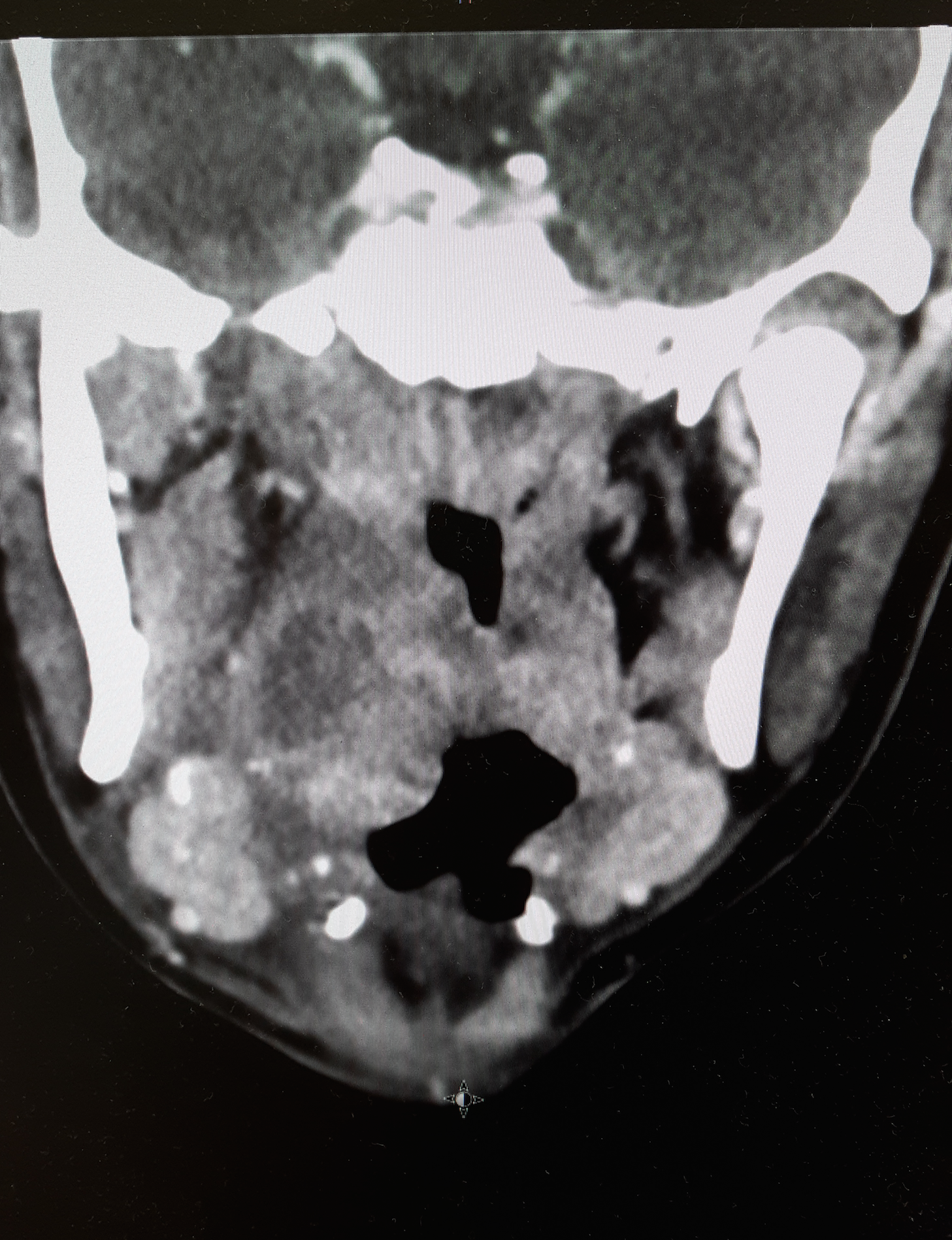
20 year-old female presents with sore throat, right throat fullness, difficulty speaking for 2-3 days. A bedside ultrasound and subsequent CT was obtained as seen below. What's the diagnosis?
Peritonsillar Abscess
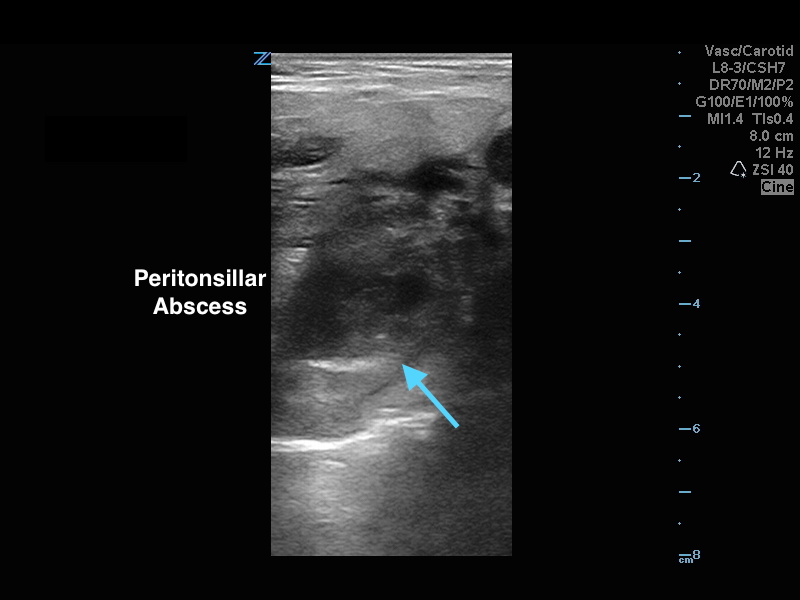
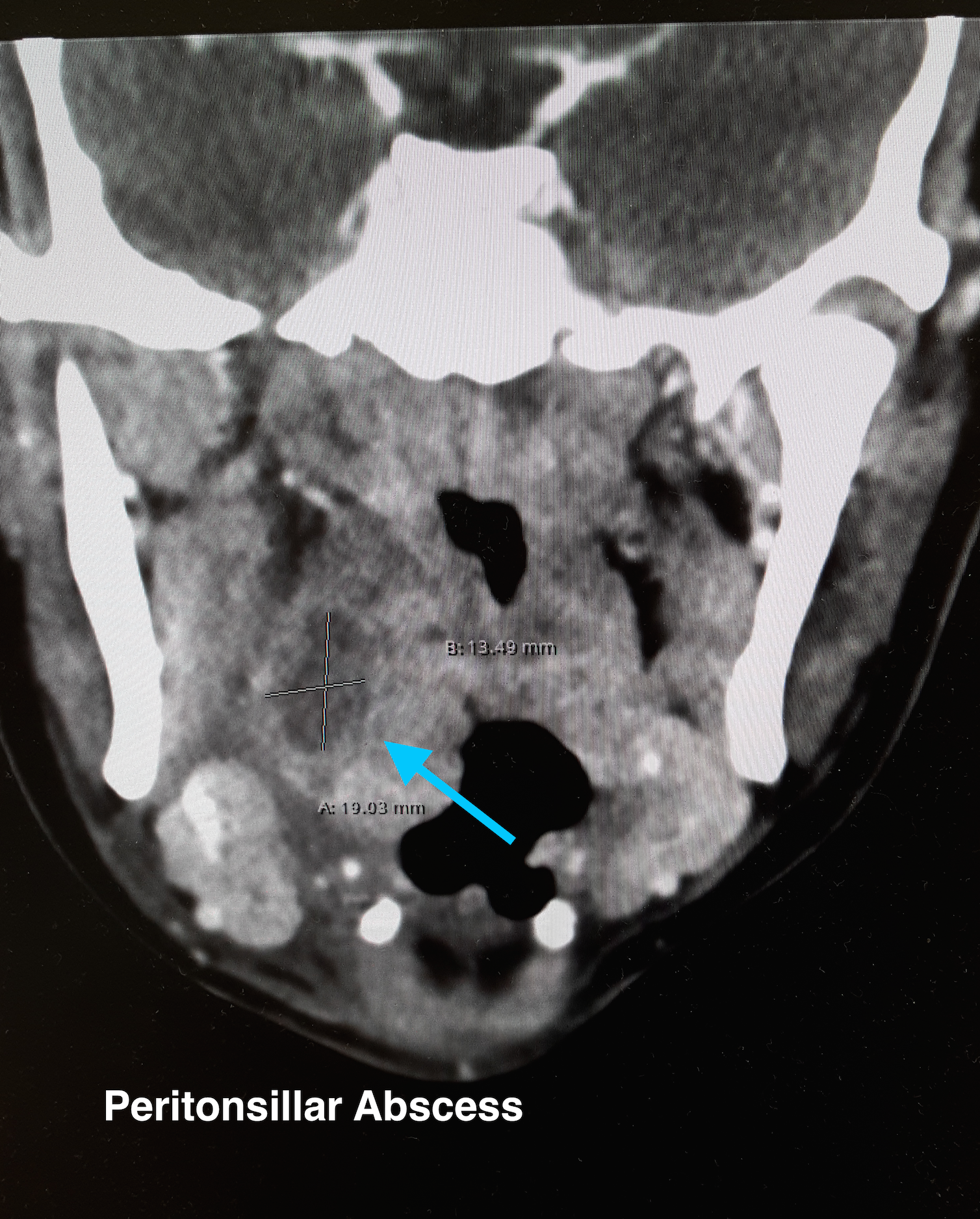
The ultrasound image is a transcutaneous approach with a linear transducer that is placed at the angle of the mandible of the affected side. This is an alternative approach to an intra-oral ultrasound with the endocavitary transducer if the patient has trismus.
Take Home Points:
How to do an intra-oral US-guided needle aspiration of PTA, check out:
http://www.ultrasoundpodcast.com/2012/01/episode-21-full-peritonsillar-abscess-podcast/
For a brief video on how to perform a transcutaneous US for PTA:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JkIYOhKCweI&t=28s
Halm BM, Ng C, Larrabee YC. Diagnosis of a Peritonsillar Abscess by Transcutaneous Point-of-Care Ultrasound in the Pediatric Emergency Department. Pediatr Emerg Care. 2016;32(7):489-92.
Rehrer M, Mantuani D, Nagdev A. Identification of peritonsillar abscess by transcutaneous cervical ultrasound. Am J Emerg Med. 2013;31(1):267.e1-3.
