Category: Critical Care
Posted: 9/11/2012 by Haney Mallemat, MD
Click here to contact Haney Mallemat, MD
40 year-old male with severe uncontrolled hypertension presents with altered mental status (head CT below). The CXR is from the same patient. What's the connection?
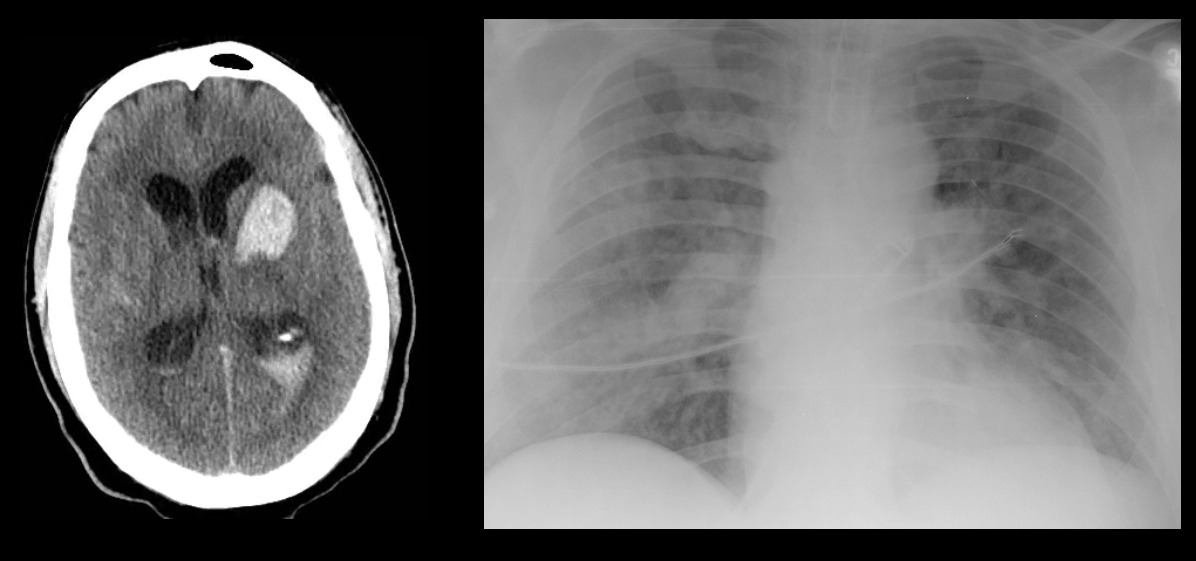
Answer: Neurogenic pulmonary edema (NPE)
NPE is defined as acute pulmonary edema following central nervous system (CNS) insult; NPE has been recognized for over 100 years, but its incidence is underreported due to a lack objective clinical criteria.
The pathophysiology of NPE is poorly understood but it is generally believed that both cardiogenic and non-cardiogenic pulmonary edema play a role. CXR (see above) demonstrates a pattern similar to acute respiratory distress syndrome (i.e., bilateral interstitial infiltrates).
CNS insults that are abrupt, rapidly progressive, and increase intracranial pressure (e.g., subarachnoid hemorrhage, intraparenchymal hemorrhage, traumatic brain injury, subdural, etc.) have the highest risk for NPE. Neural injury leads to sympathetic activation, the release of catecholamines, and one or all of the following:
Treatment of NPE includes:
Davidson, D. et al. Neurogenic pulmonary edema. Crit Care. 2012 Mar 20;16(2):212.
Follow me on Twitter (@criticalcarenow) and Google+ (+haneymallemat)
